When the world’s most advanced telescopes suddenly went dark, the global scientific community was left in the shadows.
For years, Western observatories have been the backbone of interstellar research, capturing images that fueled our understanding of the cosmos.
But in a twist worthy of a Hollywood thriller, it was China that stepped into the void, releasing high-resolution images of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS that no other nation could provide.
This isn’t just a story about a comet.
It’s a seismic shift in the balance of power in space exploration, with implications that stretch far beyond the scientific realm.

The Mystery of the Darkened Telescopes
It began quietly.
Reports started trickling in from major observatories in North America and Europe: technical glitches, unexplained outages, and a growing inability to track one of the most intriguing objects in our solar system.
3I/ATLAS, only the third confirmed interstellar visitor to our cosmic neighborhood, was slipping through our fingers.
The timing couldn’t have been worse.
Just as the comet approached its closest point to Earth, Western telescopes went offline, leaving scientists scrambling for answers.
Was it sabotage?
A freak accident?
Or simply the limits of aging infrastructure?
The truth remains elusive, but the consequences were immediate.
Vital data was lost.
Research stalled.
And for the first time in decades, the world’s scientific gaze turned elsewhere for answers.

China Steps Into the Spotlight
Enter China.
Long seen as a rising power in space, the nation has invested billions in cutting-edge technology, launching satellites, rovers, and telescopes designed to rival the best in the West.
But until now, China’s astronomical achievements had been overshadowed by the legacy of NASA and the European Space Agency.
That changed overnight.
With Western telescopes down, China’s observatories became the sole eyes on the sky.
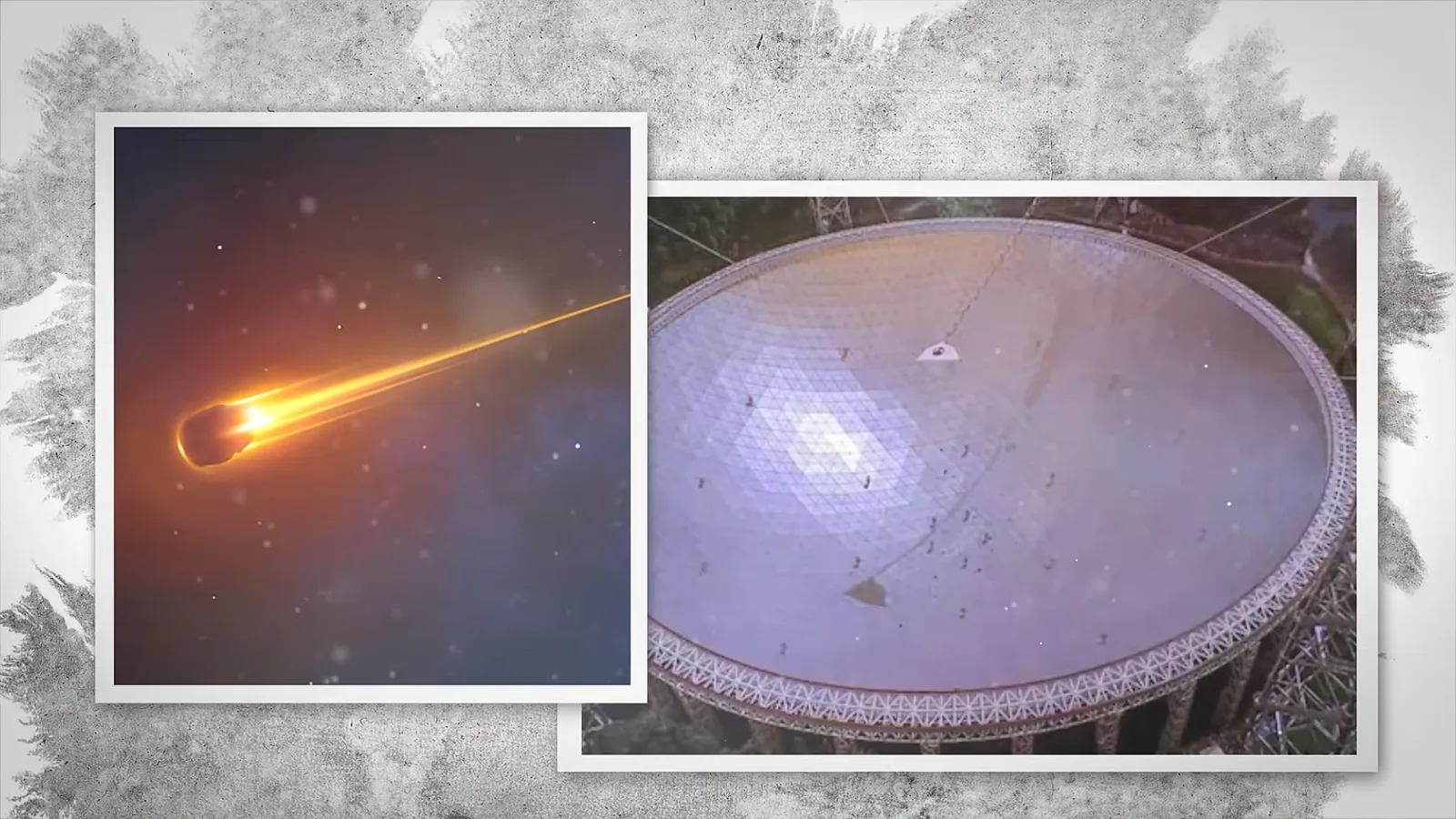
In a move that stunned the global community, Chinese scientists released a series of high-resolution images of 3I/ATLAS, revealing details never before seen.
The visuals weren’t just impressive—they were revolutionary.
For the first time, researchers could study the comet’s structure, composition, and trajectory in unprecedented detail.
The images filled a critical gap in our understanding, allowing scientists to continue their work without missing a beat.

The Science Behind the Images
What makes these images so special?
First, their clarity.
Using advanced optics and state-of-the-art sensors, China’s telescopes captured the comet in stunning detail, from its icy core to the cloud of dust trailing in its wake.
Second, their timing.
Released at the precise moment when Western data streams went dark, the images provided a lifeline to researchers desperate for information.
Third, their scope.
Chinese scientists didn’t just release a handful of photos—they published a comprehensive dataset, including infrared and ultraviolet scans, spectral analysis, and time-lapse sequences showing the comet’s movement across the sky.
This wealth of information has already led to new discoveries.
Researchers have identified unique chemical signatures in the comet’s tail, suggesting it originated from a distant star system unlike any previously studied.
Others have used the data to refine models of interstellar travel, shedding light on how such objects navigate the vast expanse between stars.

Geopolitics in the Stars
But the story doesn’t end with science.
The release of the 3I/ATLAS images has sparked a geopolitical firestorm, with analysts warning that China’s ascendancy in space could have far-reaching consequences.
For decades, the United States and its allies have dominated space exploration, setting the agenda for research, technology, and international cooperation.
China’s breakthrough challenges that status quo.
By providing essential data when others could not, China has positioned itself as an indispensable player in the new space race.
The implications are profound.
Access to high-quality astronomical data is more than a matter of scientific prestige—it’s a strategic asset.
Countries that control the flow of information can shape research priorities, influence global policy, and drive technological innovation.
China’s decision to release the 3I/ATLAS images may have been motivated by a desire to showcase its capabilities, but it also sends a clear message: the future of space belongs to those who invest in it.
The Global Response
The reaction from the international community has been mixed.
Some scientists have praised China’s openness, hailing the release of the images as a triumph of collaboration over competition.
Others have expressed concern, warning that reliance on a single nation for critical data could undermine the spirit of shared discovery that has long defined space research.
Governments are taking notice.
In Washington, lawmakers have called for renewed investment in space infrastructure, citing the outage as a wake-up call for American science.
European leaders have echoed these concerns, pledging to upgrade aging telescopes and foster closer cooperation with international partners.
At the same time, China has seized the moment to expand its influence.
Officials have offered to share data with researchers around the world, positioning their country as a hub for global astronomy.
The move has already attracted interest from developing nations eager to participate in cutting-edge research.
But it has also raised questions about the long-term balance of power in space.
Will China’s generosity lead to greater collaboration, or will it deepen divisions in an already competitive field?
Only time will tell.

The New Space Race
The release of the 3I/ATLAS images marks a turning point in the history of space exploration.
No longer can the West assume its dominance is unchallenged.
China’s technological leap has demonstrated that innovation knows no borders, and that the pursuit of knowledge is a truly global endeavor.
But the stakes are higher than ever.
As nations vie for leadership in space, the risk of fragmentation grows.
Will the quest for discovery unite us, or drive us further apart?
The answer may depend on how we respond to moments like this.
If history is any guide, competition will spur innovation, driving advances that benefit all of humanity.
But cooperation will be essential to ensure that the fruits of discovery are shared, not hoarded.
The story of 3I/ATLAS is a reminder that the universe is vast, and our understanding of it is still in its infancy.
By working together, we can unlock its secrets and chart a course toward a brighter future.
What Comes Next?
As the dust settles, scientists are already looking ahead.
New missions are being planned, with teams racing to study the next interstellar visitor before it slips away.
China’s success has inspired a wave of investment in astronomical technology, with governments and private companies scrambling to build the next generation of telescopes and sensors.
The lessons of the 3I/ATLAS episode are clear: resilience, adaptability, and collaboration are essential in a rapidly changing world.
Western observatories are upgrading their systems, determined to avoid a repeat of the blackout that left them blind at a critical moment.
Chinese researchers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, exploring new techniques for capturing and analyzing cosmic phenomena.
And around the globe, young scientists are dreaming of a future where the mysteries of the universe are within reach.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for Space Exploration
The story of China’s 3I/ATLAS images is more than a tale of technological triumph.
It’s a glimpse into the future of space exploration—a future defined by innovation, competition, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
As the world adjusts to this new reality, one thing is certain: the universe belongs to those who dare to explore it.
Whether we face the unknown as rivals or as partners will shape the destiny of our species for generations to come.
For now, the eyes of the world are fixed on the stars, and the race to unlock their secrets has only just begun.
News
New Titanic Discovery At 3800M Depth Changes Everything They Told Us!
New Titanic Discovery At 3800M Depth Changes Everything They Told Us! In the cold, dark abyss of the Atlantic Ocean,…
3I:ATLAS Is Getting Too Close To The Sun… And Something Feels WRONG!
3I:ATLAS Is Getting Too Close To The Sun… And Something Feels WRONG! Something strange is happening at the edge of…
Landslide Exposed Bunker Door, Ranger Stepped Inside and Ran Out Screaming!
Landslide Exposed Bunker Door, Ranger Stepped Inside and Ran Out Screaming! In a world filled with the ordinary, sometimes extraordinary…
Voyager 2 Sent This Transmission and JUST WARNED THE WORLD
Voyager 2 Sent This Transmission and JUST WARNED THE WORLD In an astonishing turn of events, NASA’s Voyager 2 has…
Gordon Ramsay Reveals If He’s Open to More Kids After Welcoming Sixth Child in November
Gordon Ramsay Reveals If He’s Open to More Kids After Welcoming Sixth Child in November The chef opened up about…
Gordon Ramsay Shares Plans to Take Son Oscar, 5, to Disney This Summer – But He Won’t Go on Rides
Gordon Ramsay Shares Plans to Take Son Oscar, 5, to Disney This Summer – But He Won’t Go on Rides…
End of content
No more pages to load