The Cosmic Enigma: Is 3I/ATLAS an Alien Beacon or Just Another Comet?
A mystery interstellar object has recently captured the attention of astronomers around the globe.
Dubbed 3I/ATLAS, this enigmatic visitor may very well be the oldest comet ever observed.
What has scientists in a frenzy is not just its age, but its behavior that defies all known laws of physics.
As it traverses our solar system, 3I/ATLAS is emitting intense beams of light toward the sun, changing colors like a cosmic mood ring, and following a trajectory so precise that it seems almost designed.
The implications of this discovery are staggering.

Harvard astronomers have begun to suggest that 3I/ATLAS might not be a natural celestial body at all, but rather an artificial construct from an advanced civilization.
The alarming question arises: If 3I/ATLAS can target Mars with such precision, what could happen if it turns its sights on Earth?
For weeks, scientists tracked what they initially believed was just another wandering rock from deep space.
They expected it to follow the same predictable patterns that have governed celestial bodies for billions of years.
Instead, 3I/ATLAS decided to rewrite the rulebook, leaving professional astronomers baffled and questioning their instruments.
The object has exhibited dramatic fluctuations in brightness, transitioning from barely visible to clearly detectable almost overnight, then dropping back down without any clear explanation.
These abrupt changes are not the gentle shifts typically seen with comets; they occur so rapidly that seasoned scientists are left scratching their heads.
One of the most unsettling aspects of 3I/ATLAS is that it appears to produce light directly from its surface, rather than from the typical fuzzy cloud of gas and dust surrounding most comets.
This would be akin to finding a snowball that generates its own internal lighting system—an anomaly that challenges our understanding of how comets function.
Every other space rock that visits our solar system follows predictable patterns, heating up as they approach the sun and developing tails that point away from solar radiation.
However, 3I/ATLAS seems to have thrown caution to the wind, refusing to adhere to any established behavioral norms.
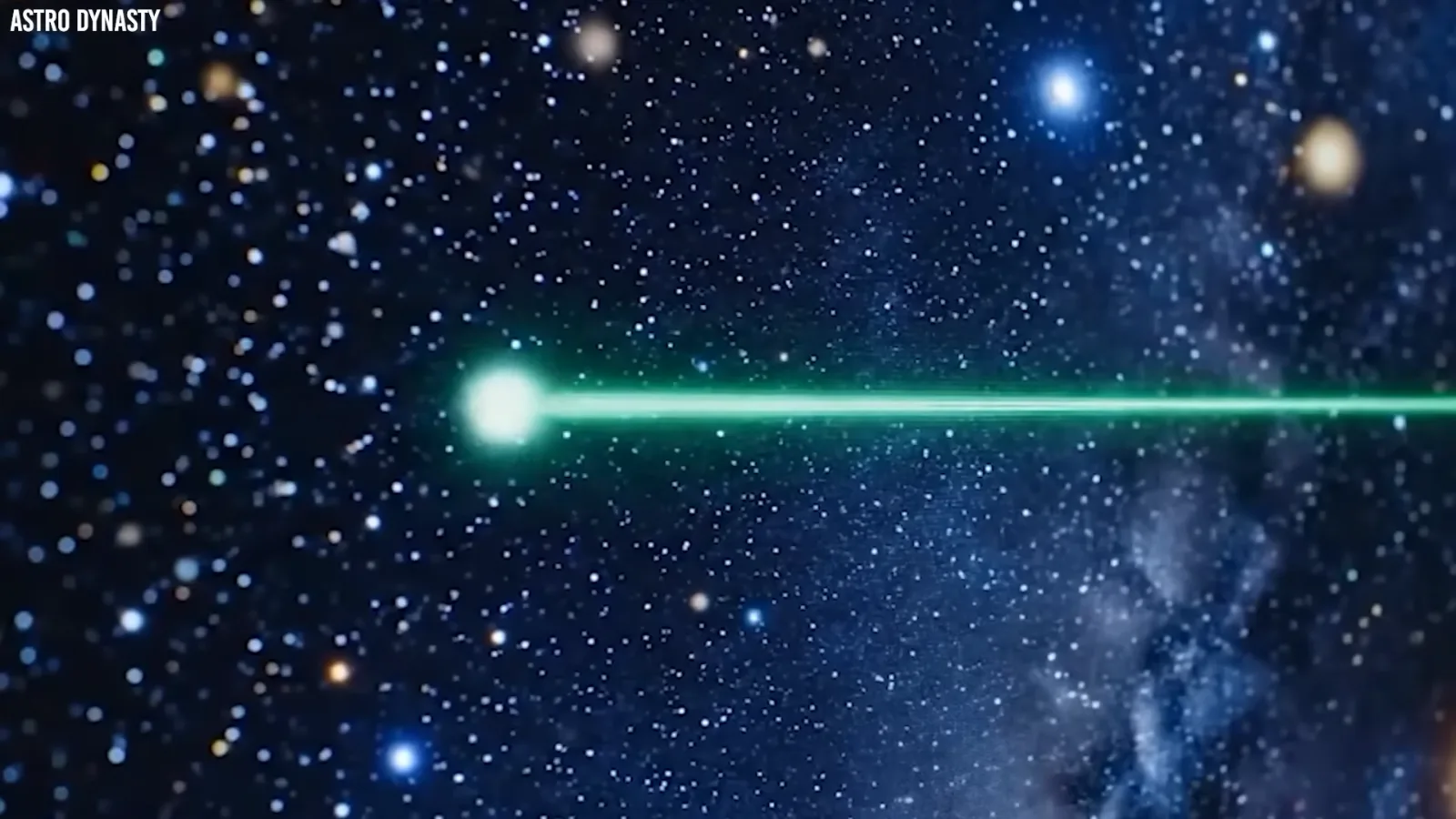

Its first act of defiance was a sudden color change from red to green as it approached Mars, occurring far too quickly and at an inappropriate distance from the sun.
This transformation does not align with the gradual, predictable chemical processes that typically govern such changes in comets.
Instead, 3I/ATLAS appears to operate according to its own internal schedule, with brightness fluctuations occurring at seemingly random intervals—creating a chaotic light curve that resembles a stock market graph rather than a smooth, predictable celestial phenomenon.
Perhaps the most mind-boggling feature of 3I/ATLAS is its ability to shoot a focused beam of light directly toward the sun.
This defies the fundamental principles of how comets behave, as every other known comet develops tails that point away from the sun due to solar wind and radiation pressure.
The fact that 3I/ATLAS is producing a forward-pointing light beam is unprecedented in the history of space exploration.
Images from the Hubble Space Telescope reveal this impossible structure extending ten times farther toward the sun than in any other direction.
Scientists have struggled to explain this phenomenon using conventional physics, suggesting that large chunks of solid material might be breaking away from the sun-facing side of 3I/ATLAS.
However, this theory requires the object to be composed of much more stable material than typical comets, which are usually described as “dirty snowballs” held together by frozen water and various ices.
The light beam’s intensity and focus imply either unknown physics at play or the involvement of artificial construction and control mechanisms.
Natural processes in space typically create diffuse, scattered light patterns rather than concentrated beams that maintain their focus across vast distances.

Adding to the mystery is the chemical composition of 3I/ATLAS, which seems to have been concocted in a cosmic laboratory without regard for basic chemistry principles.
Spectroscopic analysis revealed a mix of 87% carbon dioxide, 9% carbon monoxide, and only 4% water—an inversion of what scientists expect from a typical comet.
Finding something composed primarily of carbon dioxide gas with minimal water content is akin to discovering an iceberg made entirely of sand and metal.
The presence of isolated nickel without corresponding iron deposits further complicates the puzzle.
In space environments, these two metals usually occur together due to their similar formation conditions.
Isolated nickel suggests that 3I/ATLAS either formed in an unusual environment or is made of artificially manufactured materials that don’t occur through natural processes.
When Harvard astronomer Avi Lo suggests that 3I/ATLAS might be artificial technology rather than a natural phenomenon, the scientific community takes notice.
His hypothesis proposes that the object could be a technological mother ship releasing smaller reconnaissance probes, potentially gathering intelligence as it passes through our solar system.
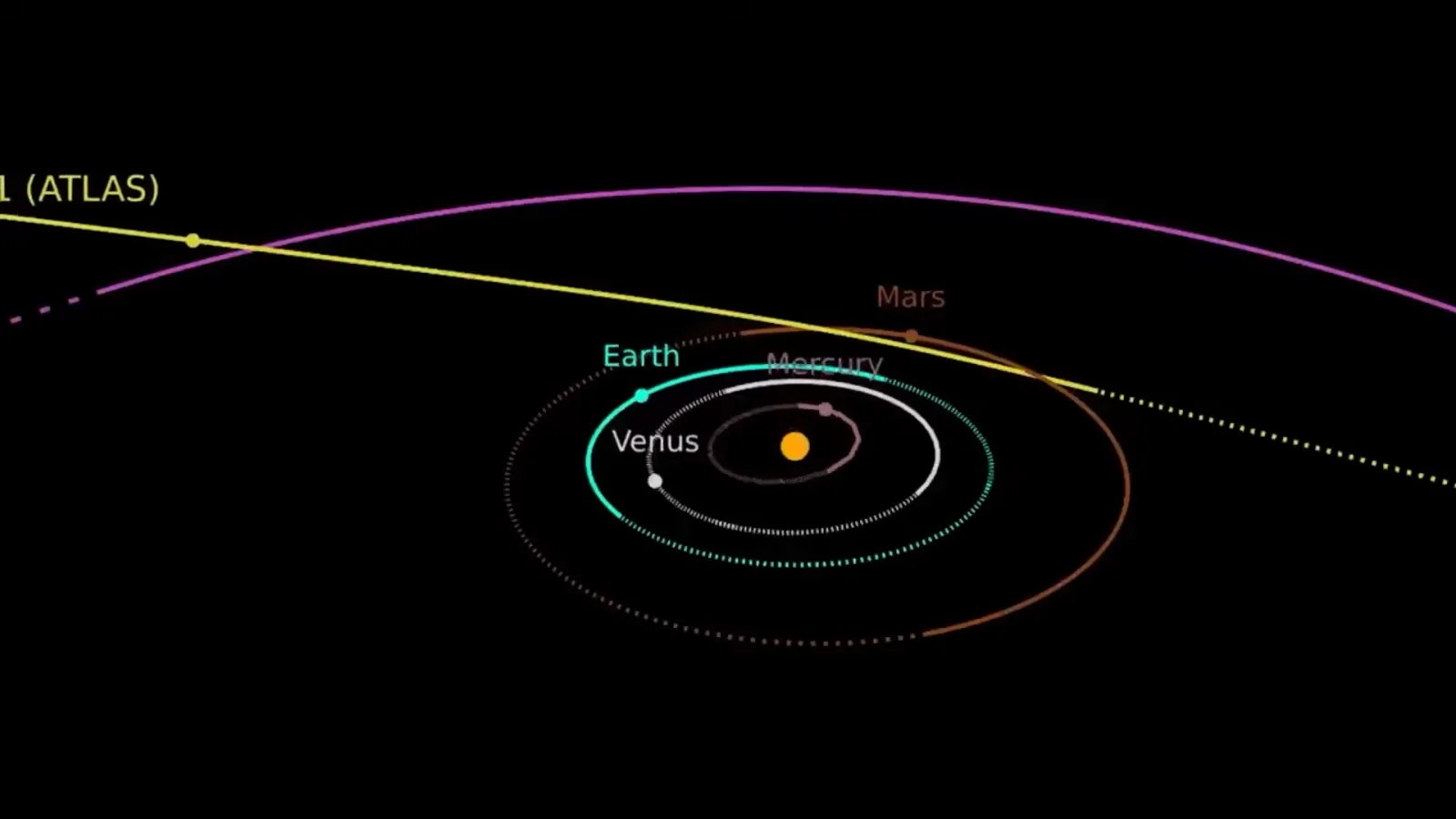
The trajectory of 3I/ATLAS is also strikingly precise, running almost parallel to the flat orbital plane of our planets.
This level of navigational accuracy is astronomically low for a random interstellar visitor, raising suspicions of intelligent control.
The object is making calculated decisions regarding its planetary encounters, passing close enough to Mars for detailed observations while avoiding Earth.
As 3I/ATLAS approaches its closest encounter with Mars on October 3, 2025, the scientific community is preparing for what could be a historic observational opportunity.
NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter will be strategically positioned to capture high-resolution images of the object, potentially revealing crucial information about its structure and light-producing mechanisms.
This flyby may determine whether 3I/ATLAS generates its own illumination through unknown processes or simply reflects solar radiation in extraordinary ways.
The data collected during this encounter could provide insight into whether humanity has discovered evidence of artificial technology from beyond our solar system or simply encountered a natural phenomenon that challenges our understanding of physics.
As we stand on the brink of this unprecedented observation, the world watches with bated breath.
The implications of 3I/ATLAS could reshape our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
Will we find evidence of extraterrestrial technology, or will we simply confront the limits of our current knowledge? Only time will tell.
News
⚡😱 The Darkest Secrets of Alaskan Bush People: Noah Brown’s Tragic Spiral 😱⚡
⚡😱 The Darkest Secrets of Alaskan Bush People: Noah Brown’s Tragic Spiral 😱⚡ In the rugged wilderness of Alaska, where…
Swamp Secrets EXPOSED 🐊💥—Troy Landry Breaks Silence on Pickle Wheat
Swamp Secrets EXPOSED 🐊💥—Troy Landry Breaks Silence on Pickle Wheat In the heart of Louisiana’s swamps, where the murky waters…
Storage Wars Secrets Exposed —The Tragedies No One Saw Coming
Storage Wars Secrets Exposed 😱—The Tragedies No One Saw Coming Storage Wars captivated audiences with its blend of excitement, drama,…
Bill Cosby’s Secret Legacy 🤫⚖️—From TV Hero to Tragic Symbol
Bill Cosby’s Secret Legacy 🤫⚖️—From TV Hero to Tragic Symbol Bill Cosby, once celebrated as America’s beloved dad, has seen…
The Rise and Fall of Brian Johnson—A.K.A.“Liver King”
The Rise and Fall of Brian Johnson—A.K.A.“Liver King” At the pinnacle of his fame, Brian Johnson, better known as the…
From Fame to Family: The Untold Battle of Jacob Landry 💔🔥
From Fame to Family: The Untold Battle of Jacob Landry 💔🔥 Jacob Landry, a familiar face on the reality series…
End of content
No more pages to load











