Overview of Comet 3I/ATLAS
Comet 3I/ATLAS is the third known object from outside our solar system that has been discovered as it passes through our celestial neighborhood.
Astronomers have classified this object as interstellar due to its hyperbolic trajectory.
This means it does not follow a closed orbit around the Sun.
When tracing the orbit of 3I/ATLAS back in time, it is clear that this comet originated from beyond our solar system.
Comet 3I/ATLAS poses no threat to Earth and will remain at a safe distance.
The closest it will come to our planet is approximately 1.8 astronomical units, which is about 170 million miles or 270 million kilometers.
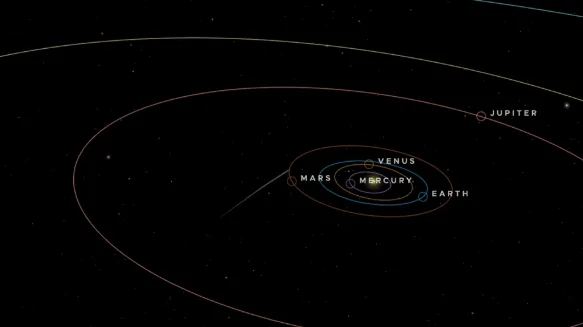
3I/ATLAS is expected to reach its perihelion, or closest approach to the Sun, around October 30, 2025, at a distance of about 1.4 AU, or 130 million miles, which is just inside the orbit of Mars.
The size and physical characteristics of this interstellar comet are currently under study by astronomers worldwide.
3I/ATLAS is anticipated to remain observable with ground-based telescopes until September 2025, after which it will be too close to the Sun for observation.
It will reappear on the other side of the Sun in early December 2025, allowing for further observation.
Discovery of Comet 3I/ATLAS
The ATLAS survey telescope, which serves as a final impact warning system for asteroids threatening Earth, first reported observations of comet 3I/ATLAS on July 1, 2025.
This telescope is funded by NASA and is located in Rio Hurtado, Chile.
Since the initial report, observations made prior to the discovery of the comet have been collected from the archives of three different ATLAS telescopes worldwide and the Zwicky Transient Facility at Caltech’s Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California.
These “pre-discovery” observations extend back to June 14, 2025.
Naming of the Comet
Comets are typically named after their discoverers, and in this case, it is named after the ATLAS survey team.
The letter “I” stands for “interstellar,” indicating that this object comes from outside our solar system.
This is the third known interstellar object, hence the number “3” in its name.
NASA’s Observations of Comet 3I/ATLAS
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured images of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on July 21, 2025, when the comet was approximately 277 million miles from Earth.
Hubble detected a droplet-shaped dust cloud emanating from the solid icy nucleus of the comet.
As Hubble tracked the comet moving along its hyperbolic orbit, stationary background stars appeared in the long-exposure images.
Continuous observations from Hubble have allowed astronomers to refine their estimates of the comet’s nucleus size.
As of August 20, 2025, the upper limit on its diameter was estimated to be 3.5 miles (5.6 kilometers), although it could be as small as 1,444 feet (440 meters).
NASA’s instruments planned to collect observational data on 3I/ATLAS include Hubble, Webb, TESS, Swift, SPHEREx, the Perseverance Mars rover, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, the Curiosity rover, Europa Clipper, Lucy, Psyche, Parker Solar Probe, PUNCH, and ESA/NASA’s SOHO and Juice missions.
Please check back for updates on observational data, schedules, or any other NASA instruments as information becomes available.
Update for September 2025

Interstellar Comet Passing Mars in Early October
NASA is actively studying the icy visitor 3I/ATLAS using space telescopes including Hubble, Webb, and SPHEREx.
As the comet passes Mars on October 3, several spacecraft will have the opportunity to observe it.
The comet is set to travel behind the Sun by the end of October and will pass Jupiter in March 2026 as it exits the solar system.
Tracking the Journey of Comet 3I/ATLAS
With NASA’s interactive application, Eyes on the Solar System, you can track comet 3I/ATLAS as it moves through our solar system and see its next destination.
News About Comet 3I/ATLAS
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope observed the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on August 6 using its Near-Infrared Spectrograph.
The research team analyzed detailed information from Webb’s data, and a preprint has been made available online.
Webb is one of several NASA space telescopes observing this fascinating comet.

Conclusion
Comet 3I/ATLAS represents a significant opportunity for astronomers to study an interstellar object.
As it approaches the Sun and makes its way through the solar system, it will provide valuable insights into the composition and behavior of comets from beyond our solar neighborhood.
The ongoing observations by various space telescopes and ground-based observatories will enhance our understanding of these celestial wanderers.
This comet not only captivates the scientific community but also the public’s imagination as it journeys through our solar system.
The excitement surrounding its discovery and the potential for new findings make 3I/ATLAS a noteworthy subject for both research and exploration.
As we continue to monitor its path, we look forward to the revelations that this interstellar visitor may bring.
News
Muslims Stormed a Church to Burn the Eucharist Then THIS HAPPENED…
I led seven men into a Catholic church to burn what Christians called the body of Christ, convinced we were…
Muslims Stormed a Church to Steal the Communion Unaware What Jesus Had Planned…
Four Muslim men walked into a church to prove Christianity was fake by taking communion and feeling nothing. What happened…
Arab Royal Mocked Jesus Publicly in Dubai, Then Dropped to One Knee in Shock vd
On December 15th, 2018, I stood before 5,000 Muslims in Dubai and spent 45 minutes mocking Jesus Christ, calling him…
A Catholic Mass Was Interrupted When Muslim Men Stole Chalice—What Happened Next Shocked Everyone
On December 8th, 2019, I walked into a Catholic church with three other Muslim men and grabbed the sacred cup…
R Kelly Thrown In “The Hole” After Alleged Prison Assassination 😳 New Trial Filing GOES LEFT
Our Kelly’s legal team just dropped bombshell allegations claiming the singer is not just serving time. He’s literally fighting for…
Diddy & Suge Knight CHARGED For Tupac’s Death
Nearly three decades after the death of Tupac Shakur, renewed debates continue to surface regarding who was ultimately responsible and…
End of content
No more pages to load












