Advanced AI analysis of Pompeii’s plaster casts reveals shocking truths about the victims’ identities, ages, and final moments. New findings overturn long-held assumptions, showing well-preserved dental health, gender misidentifications, and evidence of desperate struggle during the eruption.

In a groundbreaking revelation that has left experts reeling, advanced artificial intelligence has unearthed startling insights from the CT scans of the long-preserved victims of Pompeii.
For nearly two thousand years, these individuals, frozen in time beneath the volcanic ash of Mount Vesuvius, have told a tragic story of sudden death.
However, the latest findings challenge everything we thought we knew about their lives and deaths, forcing historians to reconsider the narrative surrounding this ancient catastrophe.
The catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius on August 24, 79 AD, engulfed the Roman city of Pompeii in a deadly cloud of ash and pyroclastic flows, burying approximately 2,000 people who were unable to escape.
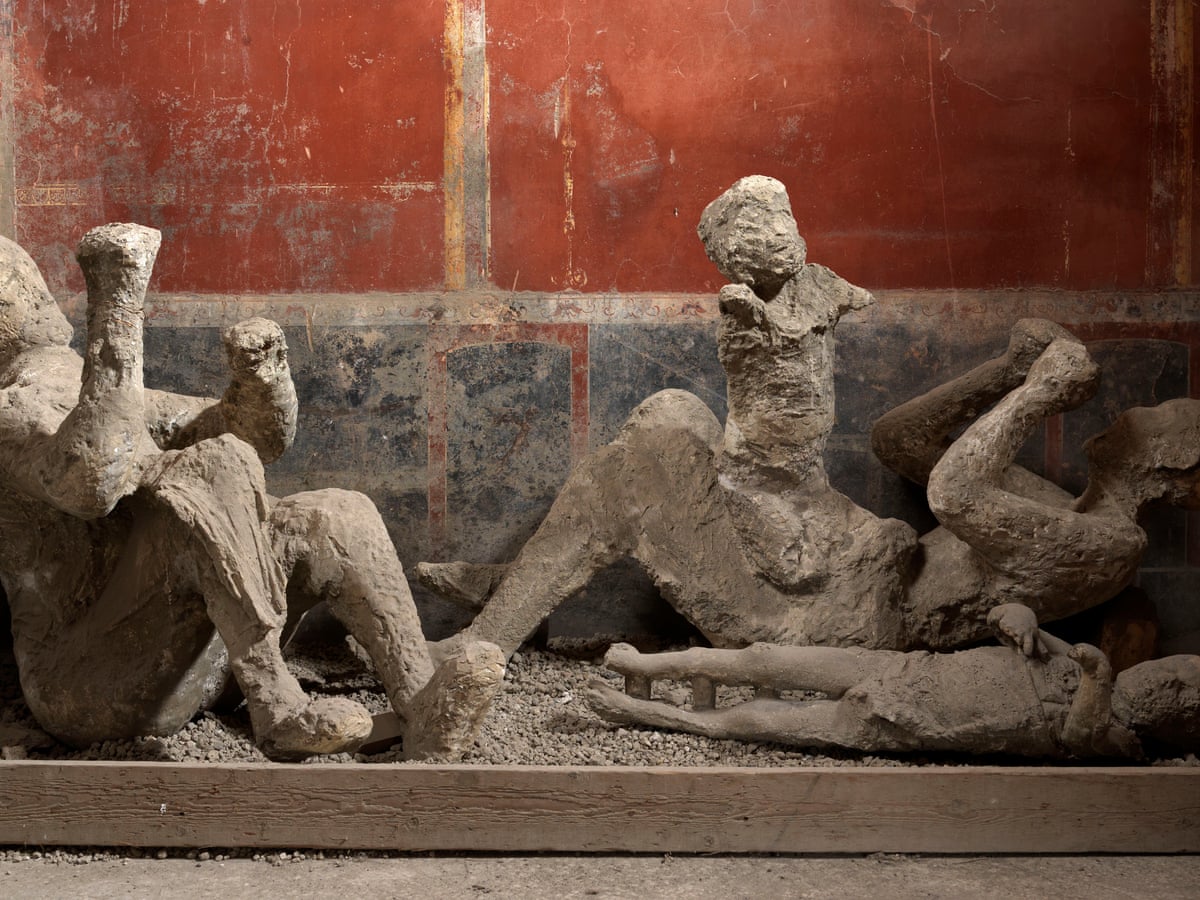
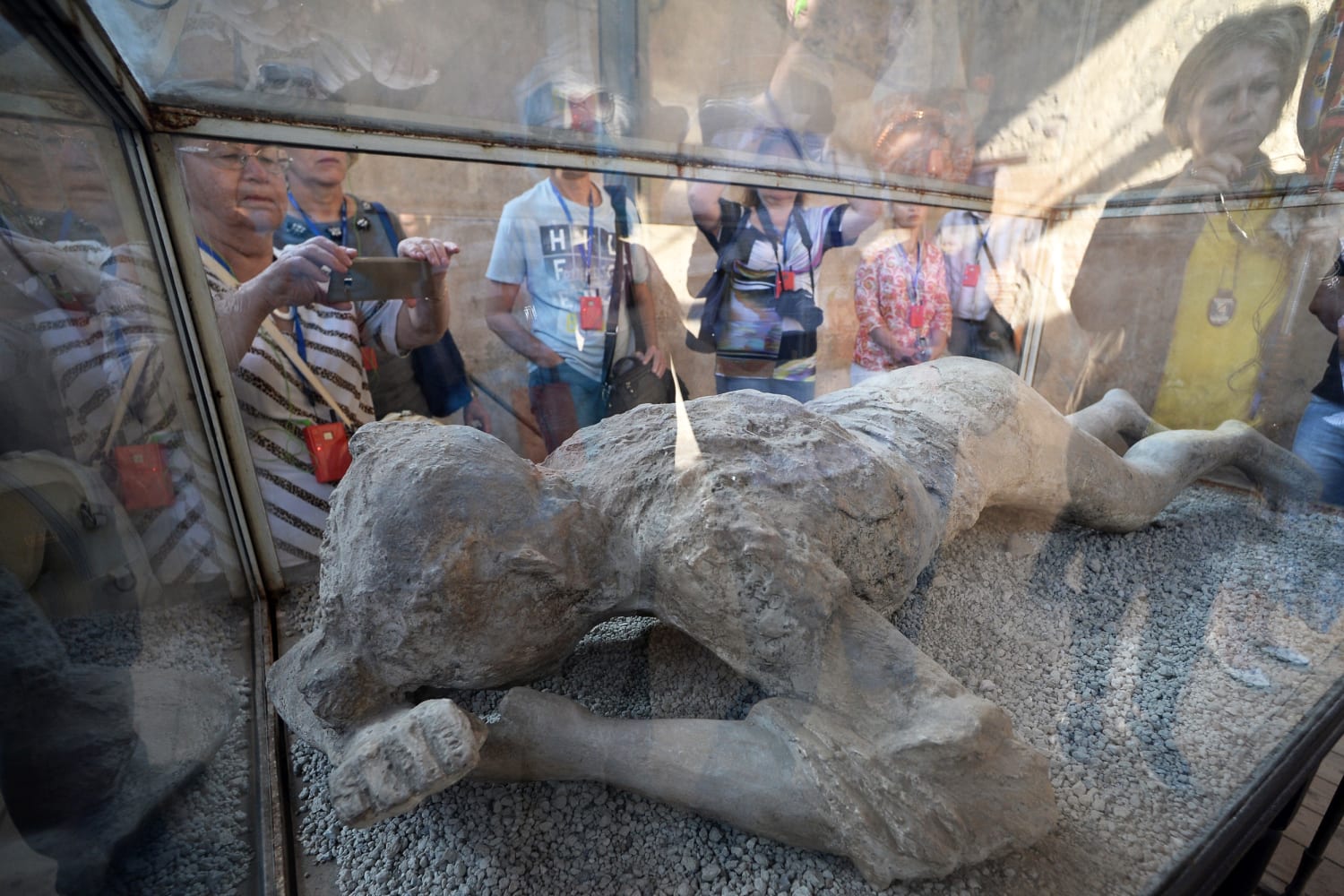
For generations, archaeologists have relied on plaster casts created by pouring material into the voids left by the decayed bodies, capturing haunting images of the victims in their final moments.
These casts have stood as poignant reminders of the disaster, depicting people crouched in corners or huddled together, seemingly at peace in their final moments. But the truth revealed by AI-enhanced CT scans is far more disturbing.

Researchers began applying CT scanning technology to Pompeii’s plaster casts in the early 2000s, but initial results were less than satisfactory.
The similarity in density between bone and plaster produced unclear images, leaving many questions unanswered. However, a groundbreaking collaboration of archaeologists, radiologists, and AI engineers in 2023 marked a turning point.
By feeding decades of CT scan data into machine learning systems, they allowed the AI to interpret the images rather than relying on human eyes, leading to astonishing results.
The AI was trained on thousands of modern skeletal scans, enabling it to recognize bone density patterns and even trace remnants of soft tissue.
When combined with contrast agents that differentiated materials within the casts, the technology produced vivid, color-coded 3D models that revealed the hidden secrets of Pompeii’s victims.
What emerged was not just a clearer picture of their skeletal remains but a complete reconstruction of their lives that contradicted centuries of assumptions.
One of the most shocking discoveries involved the dental health of these ancient Romans.
Contrary to the belief that ancient populations suffered from poor dental hygiene, the AI scans showed that many victims had remarkably well-preserved teeth, displaying minimal decay and almost no cavities.
Some individuals in their 40s and 50s had complete sets of teeth with little deterioration.

This revelation prompted researchers to investigate further, uncovering that the residents of Pompeii likely benefited from a diet rich in minerals, including naturally fluoridated water and nutrient-dense foods, which contributed to their remarkable dental health.
However, the AI’s revelations did not stop at dental health. The scans also uncovered dramatic contradictions in the identities of the victims.
A cast famous for depicting two women embracing in a final moment of despair was revealed to actually consist of two men. Skeletal analysis confirmed this, overturning long-held narratives about gender and relationships in ancient Pompeii.
This pattern of misidentification extended to other victims as well, with individuals long assumed to be elderly women turning out to be teenage boys, and presumed pregnant women revealed to be men.
Beyond individual identities, the AI scans challenged established notions of social class in Pompeii. Victims found in wealthy homes were assumed to be affluent, while those in poorer areas were labeled as commoners or slaves.
However, the AI revealed a more complex social structure, indicating that some individuals classified as servants might have been from wealthy backgrounds, while others found in grand villas showed signs of malnutrition and hard labor.

The findings also prompted a reevaluation of the ages of the victims. Many individuals previously thought to be elderly were actually middle-aged, suggesting that the demographic understanding of Pompeii’s population needed significant revision.
This raises crucial questions about why many healthy adults remained in the city during the eruption, challenging the narrative that only the poor or enslaved were left behind.
Perhaps the most unsettling revelations came from the trauma analysis conducted by the AI. The scans revealed that many victims did not die peacefully as previously believed.
Instead, evidence of defensive injuries indicated that some fought to survive, raising their arms to shield themselves from the oncoming destruction.
Others suffered catastrophic injuries from the eruption’s violent force, leading to a terrifying realization: the majority of Pompeii’s residents experienced a horrific end, rather than a tranquil demise.
The AI analysis exposed the brutal reality of the eruption, showing that many victims survived the initial waves of pyroclastic surge only to be killed by subsequent blasts.
This new understanding dismantles the comforting narrative of peaceful preservation, revealing instead the chaos and terror that accompanied the disaster.
These findings mark a pivotal moment in archaeology, demonstrating the power of technology to reveal truths that challenge our understanding of history.
The implications extend far beyond Pompeii, as museums worldwide reconsider their collections and the potential secrets hidden within preserved remains.
The use of AI and advanced imaging techniques could unlock hidden details in mummies, bog bodies, and other archaeological artifacts, transforming the field of historical research.
As researchers grapple with the ethical implications of these discoveries, questions arise about how we memorialize tragedy.
With a deeper understanding of the violent deaths of Pompeii’s victims, the debate intensifies over the display of plaster casts that have long been viewed as mere artifacts.
Should we continue to exhibit these reminders of human suffering, or does the new knowledge demand a reevaluation of how we honor those who perished?
The revelations from Pompeii serve as a powerful reminder of the complexities of history and the human experience.
As we confront the truths uncovered by AI, we must ask ourselves: do we truly know the stories of those who came before us, or are we only beginning to scratch the surface?
The journey into the past continues, and with it, the responsibility to remember and honor the lives lost in one of history’s most catastrophic events.
News
The Shocking Secret George Marshall Took to His Grave: D-Day’s Dark Truth Revealed!
George C. Marshall revealed haunting secrets about D-Day, exposing the hidden sacrifices and moral compromises behind the Allied victory. The…
Ancient Egyptian DNA Reveals Unbelievable Truths That Change Everything We Thought We Knew!
Ancient DNA from a 4,800-year-old Egyptian burial reveals surprising links to the Fertile Crescent, challenging the belief that early Egypt…
From Plague to Protein: How Africa’s Bold Locust Experiment Turned Skepticism into Sustainable Success!
Africa transformed a devastating locust plague into a sustainable protein source, turning skeptics into believers. Controlled locust farming now provides…
Shocking Discovery: Ancient DNA Links to King Arthur Unearthed in Mysterious Cave!
Archaeologists in Herefordshire have uncovered ancient DNA in a cave that may be linked to the legendary King Arthur. The…
Texas’s Bold Fish Experiment: The Unexpected Hero in the War Against Mosquitoes!
The article recounts how Texas officials successfully used mosquitofish to combat a severe mosquito outbreak that threatened public health. Initially…
After a Century in the Deep, Shackleton’s Ghost Ship Emerges from the Ice – What Lies Beneath?
The article details the stunning discovery of Sir Ernest Shackleton’s ship Endurance, found perfectly preserved beneath Antarctic ice after more…
End of content
No more pages to load