SHOCKING GENETIC REVELATION: Ancient DNA Unveils the TRUE ORIGINS of Neanderthals — They Were NOT Humans but a Completely Separate Species, Upending Centuries of Evolutionary Beliefs!

What Dark Secrets Have Been Hidden in Our Genetic Past, and How Does This Rewrite the Story of Human Ancestry? Prepare to Question Everything You Thought You Knew About Our Closest Relatives…
For centuries, Neanderthals have been portrayed as our closest extinct relatives—primitive cousins who walked the Earth alongside early Homo sapiens and contributed to the rich tapestry of human evolution.
However, recent breakthroughs in ancient DNA analysis have dramatically altered this narrative, revealing that Neanderthals were not simply early humans or a subspecies of Homo sapiens.
Instead, they were a distinct species with their own unique evolutionary trajectory, separate from modern humans.
This revelation emerged from the most comprehensive genetic study ever conducted on Neanderthal fossils, which date back tens of thousands of years.

Scientists meticulously sequenced Neanderthal genomes with unprecedented precision, uncovering genetic markers that starkly differentiate them from modern humans.
The evidence suggests that Neanderthals diverged from a common ancestor with Homo sapiens much earlier than previously believed, evolving in isolation for hundreds of thousands of years.
One of the most astonishing findings is the extent of genetic differences between Neanderthals and modern humans.
The study identified variations in genes related to brain development, immune system function, and metabolism—traits that indicate Neanderthals adapted to environments and challenges very different from those faced by early Homo sapiens.
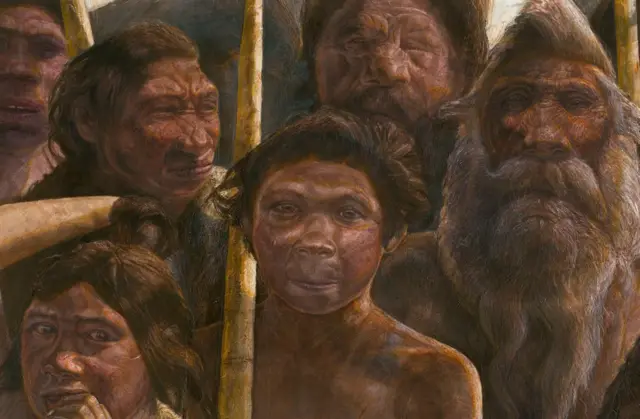

These genetic distinctions underscore that Neanderthals were not primitive versions of humans but rather a species uniquely equipped to survive in their own ecological niches.
Contrary to earlier theories that suggested significant interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans, the new data reveals that such gene flow was minimal.
While the two species coexisted and likely interacted, they maintained distinct biological identities, more akin to separate species than interbreeding populations.
This finding challenges the long-held assumption that modern humans absorbed Neanderthals into their lineage through extensive hybridization.
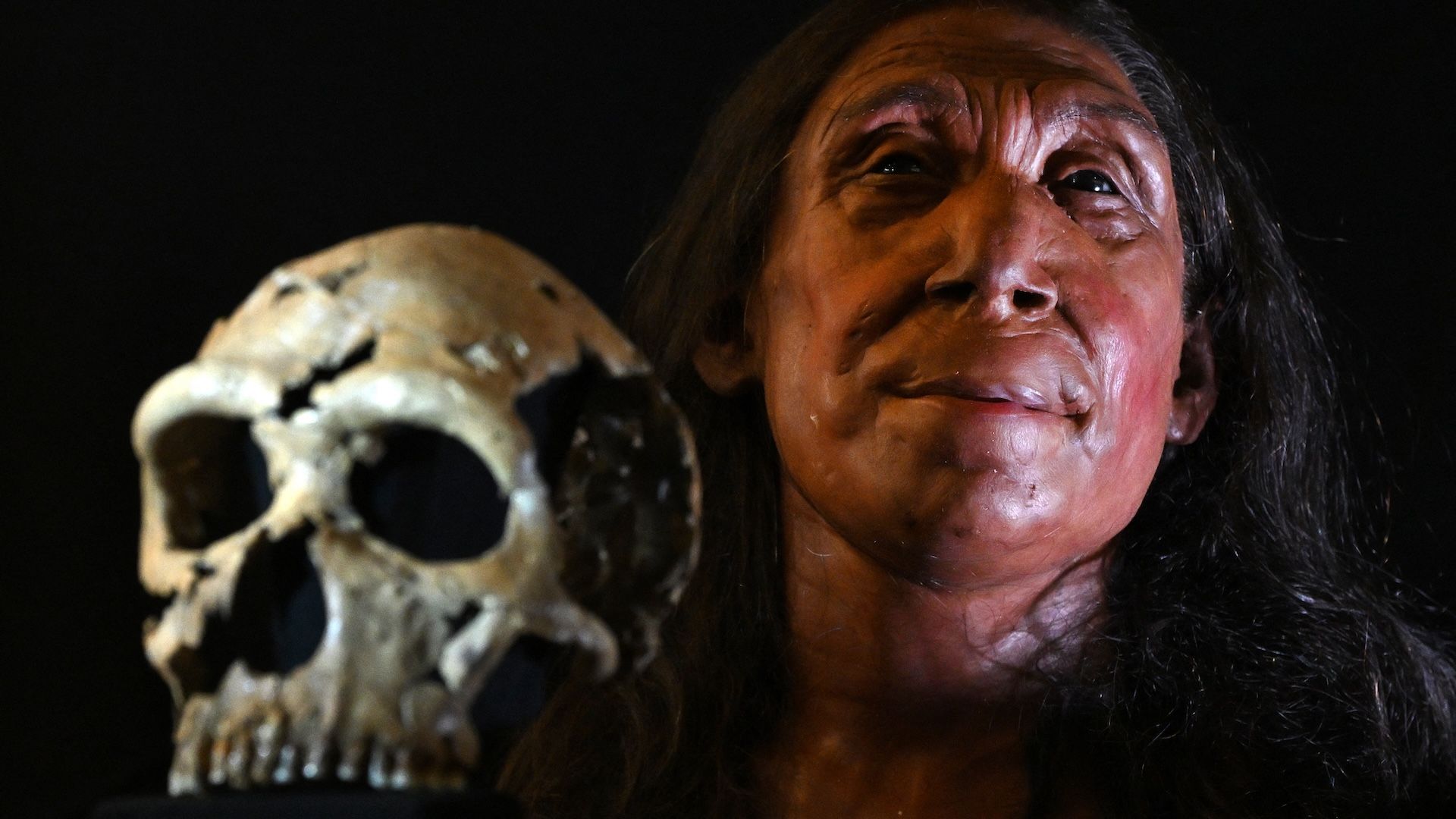

The implications of these discoveries are profound and far-reaching. They compel scientists to reconsider the simplistic view of human evolution as a linear progression culminating in Homo sapiens.
Instead, the evidence paints a complex picture of parallel evolution, competition, and coexistence between two distinct hominin species.
This paradigm shift invites new questions about how Neanderthals lived—did they develop their own languages, cultures, and technologies independent of humans?
How did their unique adaptations shape their survival strategies and eventual extinction?
Beyond the scientific community, this revelation challenges our understanding of what it means to be human.

If Neanderthals were a separate species, the boundaries defining humanity become blurred, prompting philosophical and ethical debates about identity, kinship, and our place in the natural world.
It forces us to acknowledge the rich diversity of hominin life that once thrived on Earth and to appreciate that humanity’s story is intertwined with other remarkable species.
Museums, educators, and researchers are already revising their interpretations of human history to incorporate these groundbreaking insights.
The new genetic evidence not only enriches our knowledge of the past but also inspires a deeper respect for the complexity and resilience of life on our planet.
As scientists continue to delve into ancient DNA and uncover more secrets from prehistory, the story of human evolution grows ever more intricate and fascinating.

Neanderthals, once dismissed as mere primitive cousins, emerge as a distinct and remarkable species with their own legacy—a legacy that challenges and enriches our understanding of life itself.
This discovery marks a pivotal moment in the study of human origins, reminding us that the past is full of surprises and that the quest to understand ourselves is far from over.
The true story of the Neanderthals is a testament to the diversity and adaptability of life, urging us to rethink the evolutionary journey that shaped our world.
Stay tuned as ongoing research continues to illuminate the enigmatic lives of Neanderthals and reshapes the epic saga of human ancestry—revealing a past more complex and extraordinary than we ever imagined.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
News
🧿BREAKING: US NAVY FLIGHT 19 FOUND 75 YEARS AFTER THE BERMUDA TRIANGLE MYSTERY MAY FINALLY BE SOLVED! ✈️🌊🕵️♂️
BREAKING: U.S. NAVY FLIGHT 19 FOUND AFTER 75 YEARS — THE BERMUDA TRIANGLE MYSTERY MAY FINALLY BE SOLVED! For over…
🧿AFTER 11 YEARS, UNDERWATER DRONE FINALLY UNCOVERS MH370’S HIDDEN SECRETS — SHOCKING DISCOVERY REWRITES HISTORY! 🌊✈️🔍
AFTER 11 YEARS, UNDERWATER DRONE FINALLY UNCOVERS MH370’S HIDDEN SECRETS — SHOCKING DISCOVERY REWRITES HISTORY! Eleven years after the baffling…
🧿3I/ATLAS JUST DID THE IMPOSSIBLE NEAR MARS — NASA BAFFLED, SCIENTIFIC COMMUNITY IN SHOCK! 🚀🔴👽
3I/ATLAS JUST DID THE IMPOSSIBLE NEAR MARS — NASA BAFFLED, SCIENTIFIC COMMUNITY IN SHOCK! In a stunning and unprecedented event,…
🧿ELON MUSK DROPS BOMBSHELL: “3I/ATLAS IS AN ALIEN SPACECRAFT — WE MUST RUN OR DESTROY IT!” 🌌🚀💥
ELON MUSK DROPS BOMBSHELL: “3I/ATLAS IS AN ALIEN SPACECRAFT — WE MUST RUN OR DESTROY IT!” WORLD ON EDGE AS…
🧿AMAZING AND TERRIFYING REVELATION: JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE CONFIRMS 3I/ATLAS IS ON A DIRECT COLLISION COURSE WITH EARTH — GLOBAL PANIC ERUPTS AS SCIENTISTS WARN OF UNPRECEDENTED CATASTROPHE! 🌍🚀💥
AMAZING AND TERRIFYING REVELATION: JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE CONFIRMS 3I/ATLAS IS ON A DIRECT COLLISION COURSE WITH EARTH — GLOBAL PANIC…
🧿“IT WAS WATCHING US” — Underwater Robots Make CHILLING Discovery in Shackleton’s Frozen Graveyard Beneath Antarctic Ice! 🧊🤖⚠️
“It Was Watching Us” — Underwater Robots Make Chilling Find in Shackleton’s Frozen Graveyard Beneath Antarctic Ice That Could Rewrite…
End of content
No more pages to load