🦴 Hidden in a Well Since 1933! The Mysterious ‘Dragon Man’ Skull Could Rewrite Human History Forever 🧠🌍
The year was 1933.
In Harbin, a cold industrial city in northeastern China, a group of workers was dredging up river mud when they stumbled across something absolutely unthinkable: a massive human-like skull, unlike anything
they’d ever seen.
It was too strange to make sense of—and maybe too dangerous to share.
Fearing trouble or ridicule, one of the workers wrapped the skull up and hid it in an abandoned well, keeping its existence a secret until his dying breath.
It wasn’t until 2018, decades later, that he confessed the discovery to his grandchildren.
They retrieved the skull and handed it over to scientists—who were stunned by what they found.
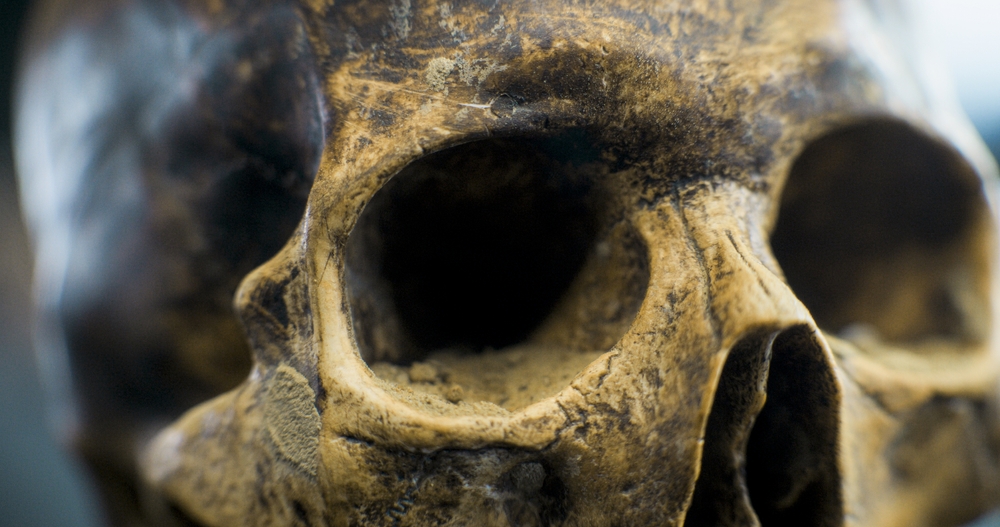
Now known as Homo longi—or more sensationally, Dragon Man—this skull immediately puzzled researchers.
It had a bizarre mix of traits: a heavy brow ridge, delicate cheekbones, a massive cranium nearly 26 inches around (comparable to a gorilla), and teeth that looked straight out of a nightmare.
It wasn’t just big—it was beautifully preserved and unlike anything seen before.
Most crucially, the features seemed shockingly modern, raising the possibility that this being wasn’t some distant ancestor, but possibly our closest evolutionary relative—even closer than the Neanderthals.
But what exactly is Dragon Man?
To find out, a global team of researchers examined 95 ancient skulls, jaws, and teeth from across the hominin spectrum.
Using a supercomputer, they built billions of possible evolutionary trees and relationships, mapping out the simplest, most likely connections.
The result? Dragon Man didn’t fit into any known group.
He was something new—a previously unknown species or subspecies that branched off from our shared ancestors and may have lived alongside modern humans in East Asia more than 146,000 years ago.
Some scientists argue that Dragon Man may actually be a Denisovan—a mysterious group of ancient humans discovered only in 2008 from a tiny fragment of a child’s finger bone in Denisova Cave in Siberia.
DNA tests showed the girl belonged to a whole new human species, related to Neanderthals but genetically distinct.
Since then, only a handful of Denisovan fossils have surfaced, most too incomplete to paint a clear picture.
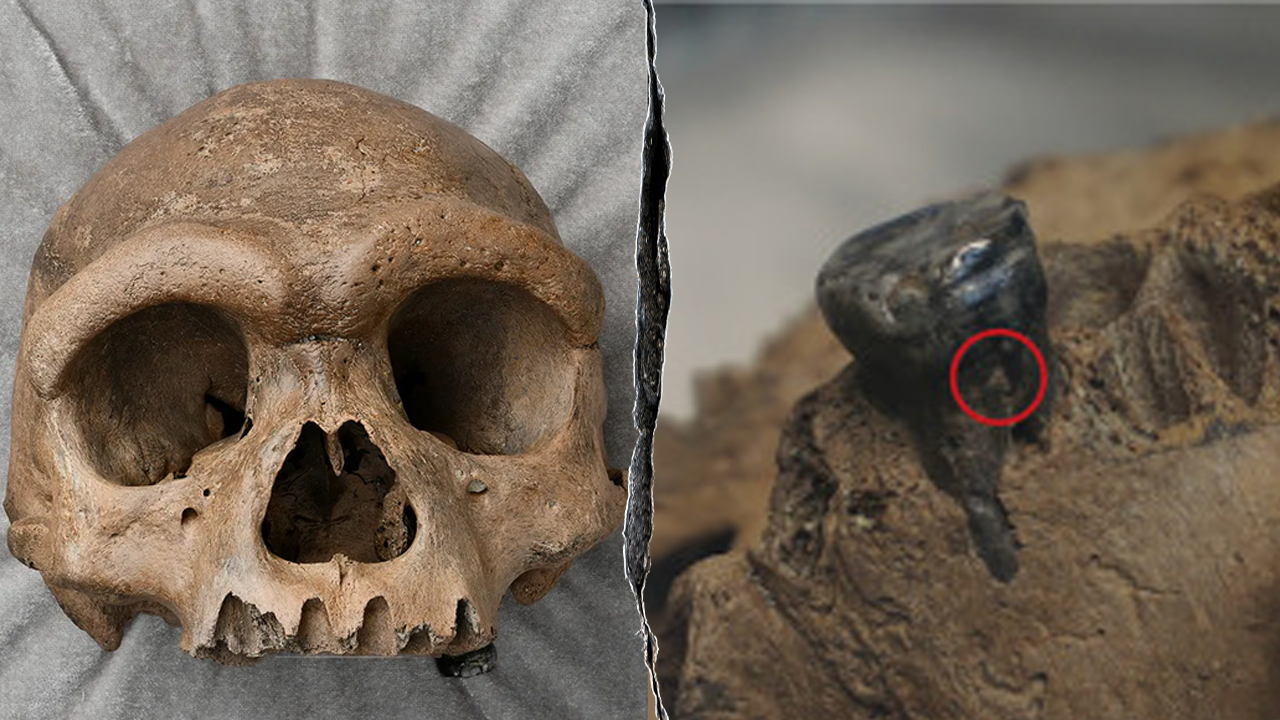

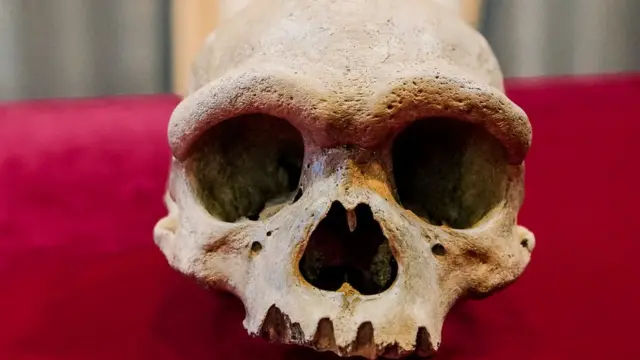
But Dragon Man’s skull—nearly complete and colossal in size—might be the key to finally understanding this elusive lineage.
Still, there’s a problem: the Harbin skull has no jaw, and the most closely matching Denisovan fossil is—you guessed it—a jawbone found in Tibet in 2019.
Without a direct comparison, the Dragon Man-Denisovan link remains a tantalizing theory, but not yet a fact.
Yet the similarities in age, geography, and physical traits have made many researchers strongly suspect that Dragon Man might be our first real look at what a Denisovan actually looked like.
To bring him to life, Brazilian scientist Cicero Moraes created a 3D digital facial reconstruction based on the skull.
Using advanced scans and techniques involving modern human and chimpanzee facial structures, he filled in the missing parts using data from a Homo erectus skull.
The result? A strikingly lifelike face with thick brows, deep-set eyes, and a jawline that screams primal power.
He looks more like a character from Game of Thrones than a distant cousin—but this face may be one of the most accurate reconstructions of an extinct human ever created.
Dragon Man’s huge head and robust build may have been evolutionary adaptations to the harsh, icy climate of Harbin, which remains freezing cold even today.
Some scientists suggest his body was optimized for survival, with physical traits that helped him outlive other ancient humans in unforgiving environments.
And this raises the question: Why did he disappear?
The answer might lie in how ancient humans lived.
Denisovans and Neanderthals are believed to have lived in small, isolated groups, with little genetic diversity.
This could have led to inbreeding and increased vulnerability to disease or environmental change.
In contrast, Homo sapiens—our species—thrived in larger, more connected social networks, sharing tools, ideas, and innovations that helped us adapt rapidly to changing conditions.
This “social advantage” might have been the deciding factor that allowed us to survive while Dragon Man and his relatives faded into extinction.
But not all of their legacy disappeared.
As modern humans moved into East Asia, they interbred with Denisovans, passing their DNA down through generations.
Today, many people in Southeast Asia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea still carry Denisovan DNA.
Some researchers believe there were actually three distinct Denisovan groups, one of which may have lived in New Guinea as recently as 15,000 years ago—the last ancient human species to share the planet with
us.

That revelation alone is mind-blowing: while Egyptian pyramids were still a distant dream, other species of human were walking the Earth.
That’s not prehistoric—it’s almost recent history.
Dragon Man’s discovery is also part of a bigger picture.
Asia, once overlooked in paleoanthropology, is now emerging as a hotspot for early human evolution.
From the Homo luzonensis in the Philippines to Denisovan genes found in Tibetan populations, the continent is yielding clues that our origin story is far more complex than the tidy “Out of Africa” model once
suggested.
And with every discovery, more mysteries emerge.
Why did some ancient humans survive longer than others? How much of their DNA still lives on in us? And what other secrets are buried in caves, rivers, and abandoned wells—waiting to be found?
The truth is, we may have barely scratched the surface of human evolution.
The Dragon Man skull reminds us that the story of “us” is not finished—not by a long shot.
It’s being rewritten with every new find, and each one shakes the foundations of what we thought we knew.
So next time someone says we’ve got human history all figured out, just remember: a skull hidden in a well for 90 years might have changed everything.
News
NASA Engineer Claims His New Engine Breaks the Laws of Physics—Scientists Are Stunned
🚀 NASA Engineer Claims His New Engine Breaks the Laws of Physics—Scientists Are Stunned 😱🧪 Meet David Burns, a long-time…
Scientists Just Found a “Lost Continent” Near Canada—And It’s Breaking All the Rules of Geology
🌎 Scientists Just Found a “Lost Continent” Near Canada—And It’s Breaking All the Rules of Geology 😱📡 Let’s get one…
Plane Vanishes in 1954 and Lands in 1989 With 92 Skeletons Onboard – What Really Happened?!
✈️ Plane Vanishes in 1954 and Lands in 1989 With 92 Skeletons Onboard – What Really Happened?! 💀⏳ It all…
The Banned Book That Reveals How the World Will End – And Why the CIA Hid It for 50 Years
📖 The Banned Book That Reveals How the World Will End – And Why the CIA Hid It for 50…
“I Was Gone for 10 Days But Only Drove for 3 Hours” – Man Claims Aliens Took Him to Another Planet… and It Gets Crazier
🛸 “I Was Gone for 10 Days But Only Drove for 3 Hours” – Man Claims Aliens Took Him to…
This Is Why the Ethiopian Bible Was BANNED! Hidden Books, Ancient Secrets & The Truth They Didn’t Want You to See
📕This Is Why the Ethiopian Bible Was BANNED! Hidden Books, Ancient Secrets & The Truth They Didn’t Want You to…
End of content
No more pages to load












