Terrifying Discovery: Chinese Scientists Capture Signals from Inside a Black Hole — NASA in Panic Mode
In a groundbreaking development that has sent shockwaves through the scientific community, a Chinese space telescope has reportedly captured what appears to be visual data from inside a black hole for the very first time.
This extraordinary achievement not only provides real observational evidence about these enigmatic cosmic phenomena but also challenges our fundamental understanding of space, time, and matter.
What lies within the depths of a black hole has long been a mystery, but the findings from this telescope may alter the very fabric of our scientific knowledge.

When we think of black holes, we often envision dark voids that consume everything in their path, including light.
This perception is not entirely inaccurate.
A black hole is defined by its event horizon, the boundary beyond which nothing can escape its gravitational pull.
Once any matter or light crosses this threshold, it is irrevocably drawn towards the center, known as the singularity, where the laws of physics as we know them cease to function.
Just outside the event horizon lies the accretion disk, a chaotic swirl of superheated gas and dust that glows with intense radiation.
This region can reach millions of degrees, emitting X-rays and other forms of energy.
While we cannot observe the black hole itself, we can see the glowing material in the accretion disk as it spirals toward oblivion.
Beyond the accretion disk is the photon sphere, where gravity is so intense that light can orbit the black hole multiple times.
This area creates a distorted view of the universe, allowing for bizarre visual phenomena.
At the heart of the black hole is the singularity, a point of infinite density where all the mass is concentrated, presenting a profound mystery that has baffled scientists for decades.
For years, black holes were considered invisible entities, detectable only by their gravitational influence on nearby matter.
However, this perception began to shift with the advent of modern telescopes.
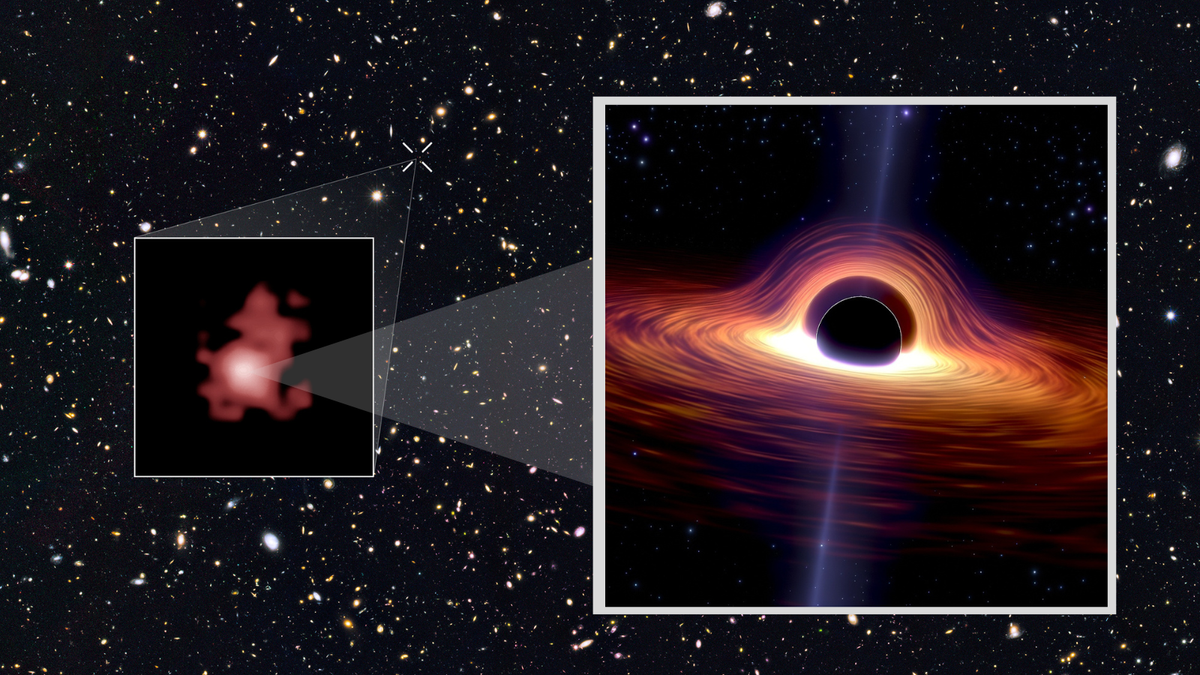
In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) made history by capturing the first real image of a black hole located in the galaxy M87, approximately 55 million light-years away.
This image revealed a dark silhouette surrounded by a glowing ring of light, confirming predictions made by Einstein’s theory of relativity.
In 2022, the EHT provided another significant breakthrough by imaging the black hole at the center of our own galaxy, Sagittarius A*.
Despite being closer in proximity, this black hole proved more challenging to observe due to its smaller size and dynamic environment.
Nevertheless, the resulting image showcased a similar structure, further solidifying our understanding of these cosmic giants.
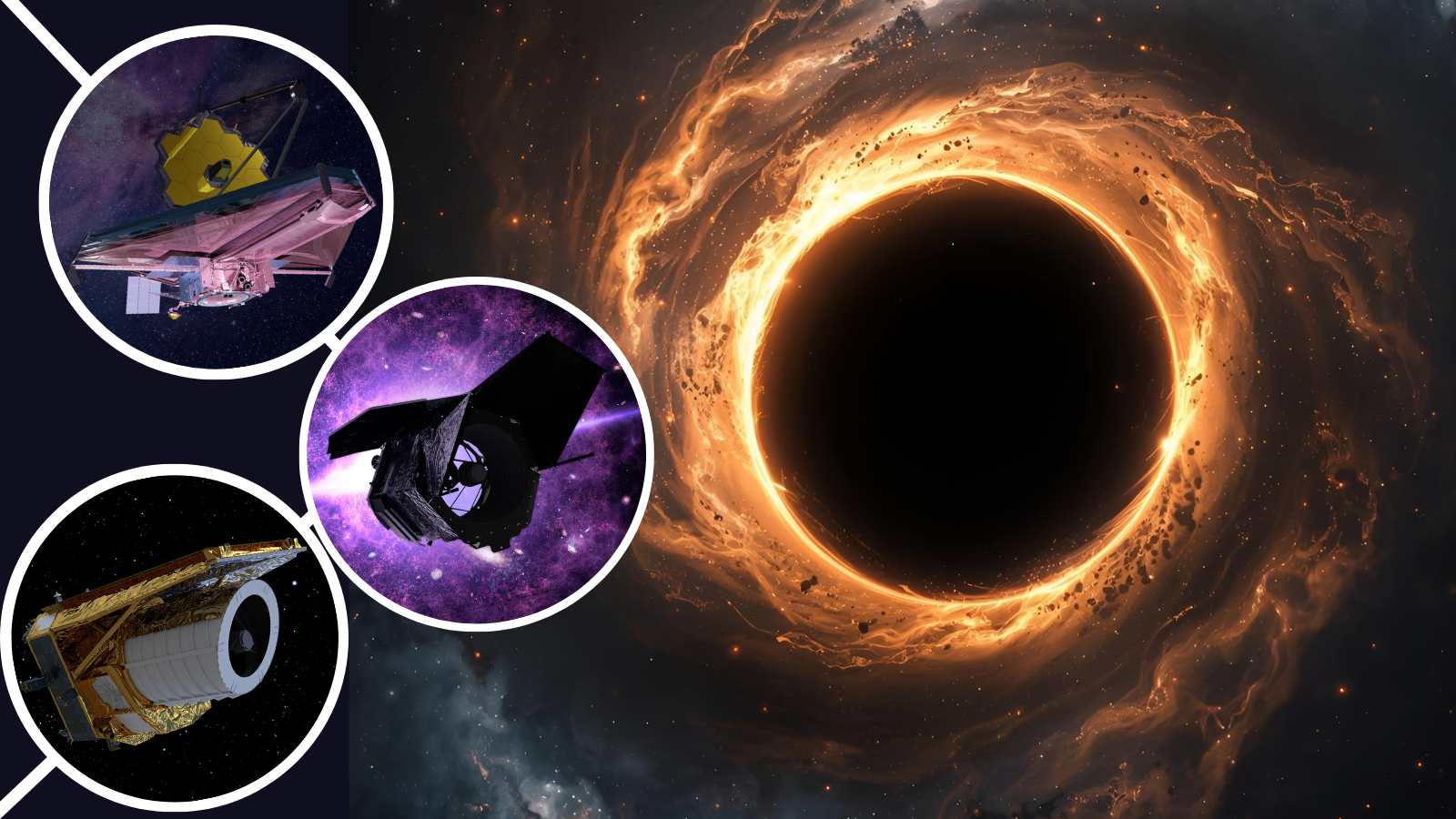
The launch of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has revolutionized our ability to study black holes.
Prior to JWST, the regions surrounding black holes were obscured by cosmic dust, limiting our observations.
However, JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities have allowed scientists to peer through this veil, revealing how black holes consume matter in real time.
One of the most remarkable discoveries made by JWST involves a supermassive black hole found in the galaxy LRDZ 8.
6, which existed just 570 million years after the Big Bang.
This black hole was surprisingly massive and active, challenging existing models of black hole formation.
The data collected from JWST has provided vital insights into the accretion processes occurring near black holes, allowing scientists to infer their mass, spin, and feeding patterns.
The images and data captured by the Chinese telescope and JWST have opened a new frontier in our understanding of black holes.
For the first time, we are beginning to glimpse the chaotic processes occurring just outside the event horizon.
The observations reveal that black holes are not silent voids; they are dynamic entities that shape their surroundings through powerful gravitational forces.
As gas and dust spiral inward, they heat up and emit radiation across various wavelengths, creating brilliant signals that astronomers can detect.
Additionally, flares of high-energy radiation have been observed, indicating magnetic turbulence and shock waves near the event horizon.
In some cases, black holes even eject jets of particles moving at nearly the speed of light, influencing the formation of stars and the evolution of galaxies.
However, despite these advancements, the interior of a black hole remains shrouded in mystery.
The event horizon marks a fundamental boundary in our understanding of reality.
Once matter crosses this threshold, it is lost to observation, and the nature of what lies beyond is still undefined.
The implications of these discoveries extend far beyond mere observation.
Black holes serve as testing grounds for the laws of physics, particularly Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
The extreme conditions near a black hole push our current models to their limits, prompting scientists to explore new theories that could reconcile quantum mechanics with relativity.
One of the most pressing questions remains the information paradox: If information is lost when matter falls into a black hole, how does this reconcile with the principles of quantum mechanics? Theoretical frameworks, such as quantum gravity and concepts like wormholes and white holes, are being explored to address these mysteries.
The recent findings from the Chinese telescope and JWST represent a monumental leap forward in our understanding of black holes.
While we may never directly observe the interiors of these enigmatic entities, the data we are gathering is reshaping our knowledge of the universe.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, the collaboration between global observatories and advanced telescopes will be crucial in unraveling the mysteries of black holes.
Each discovery brings us closer to understanding the fundamental nature of reality and the forces that govern our universe.
The journey into the abyss of black holes has only just begun, and what we uncover in the coming years may forever change our perception of space, time, and the very fabric of existence.
As we stand on the brink of these revelations, one thing is certain: the quest to understand black holes is not just about what lies within but about the profound questions that challenge the essence of our understanding of the universe itself.
News
How One Woman Saved Eminem’s Life—and Sparked a Movement of Hope! 🙌🔥
How One Woman Saved Eminem’s Life—and Sparked a Movement of Hope! 🙌🔥 The crowd at Detroit’s Ford Field…
Uncovered After 438 Years: The Shocking Truth Behind America’s Lost Colony! 🏝️😱
Uncovered After 438 Years: The Shocking Truth Behind America’s Lost Colony! 🏝️😱 Welcome to Beardy Bruce Lee Central! Today, we’re…
The Untold Story of Bruce Lee’s Training: Joe Lewis Finally Speaks After Decades🥋🔥
The Untold Story of Bruce Lee’s Training: Joe Lewis Finally Speaks After Decades🥋🔥 Welcome to Beardy Bruce Lee Central! Hey…
Inside Bruce Lee’s World: Chuck Norris Reveals Untold Stories of Their Legendary Fight 🥋🔥
Inside Bruce Lee’s World: Chuck Norris Reveals Untold Stories of Their Legendary Fight 🥋🔥 Welcome to Beardy Bruce Lee Central!…
The Untold Story of Diana and Camilla — What the Royal Chef Saw Will Shock You
The Untold Story of Diana and Camilla — What the Royal Chef Saw Will Shock You In a stunning revelation,…
Luxury, Fear, and Tyranny: Hitler’s Maid Finally Exposes Life Behind Closed Doors at the Berghof
Luxury, Fear, and Tyranny: Hitler’s Maid Finally Exposes Life Behind Closed Doors at the Berghof Today, the Hamburg radio announced…
End of content
No more pages to load