Ray’s Astrophotography EXPOSES: Is 3I/ATLAS More Than Just a Comet?
In the realm of astrophysics, few things capture the imagination quite like the discovery of interstellar objects.
Recently, independent astrophotographer Ray has made waves with his observations of 3I/ATLAS, an object that has sparked debate among scientists and enthusiasts alike.
What Ray has uncovered challenges the conventional understanding of this interstellar visitor, suggesting that it may not be a comet at all.
In this article, we’ll delve into Ray’s findings, the implications of his research, and why it matters for our understanding of the cosmos.
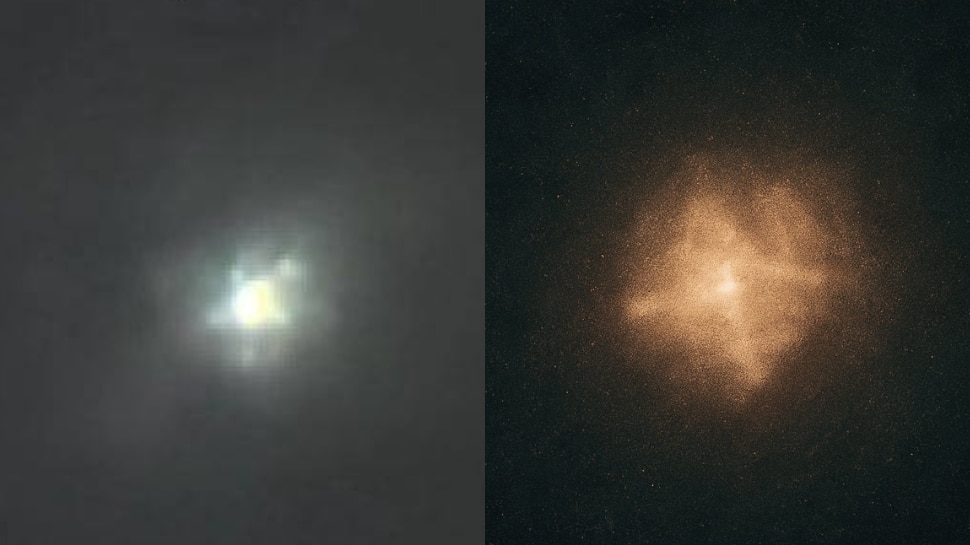

From the outset, Ray has been intrigued by the peculiar characteristics of 3I/ATLAS.
Initially observed as a comet, its behavior and appearance have led Ray to question whether it fits neatly into that category.
“It looks odd.
It looks very different,” Ray remarks, emphasizing the difficulties he’s faced in classifying this object.
Despite multiple attempts to capture its essence through photography and data analysis, he has found inconsistencies that defy standard cometary behavior.
Ray’s meticulous approach contrasts sharply with the more traditional methods employed by major space agencies.
While institutions often prefer to categorize objects as either comets or asteroids, Ray’s independent research allows him to explore the possibility that 3I/ATLAS could be something entirely new.
His willingness to entertain unconventional hypotheses is a hallmark of true scientific inquiry.
Ray’s observations highlight a crucial aspect of scientific research: the importance of independent inquiry.
Unlike institutional astronomers, who may be constrained by funding and bureaucratic protocols, Ray is free to ask the tough questions.
As he sifts through scientific papers and analyzes data, he becomes a voice for those who feel that the establishment is too quick to dismiss anomalies that don’t fit established frameworks.
This independent perspective is vital, especially when dealing with phenomena that challenge our understanding of the universe.
Ray’s assertion that 3I/ATLAS could be an alien spacecraft, while speculative, underscores the need for open-mindedness in scientific exploration.
If trained observers like Ray are detecting inconsistencies, it raises important questions about what else might be overlooked in the rush to categorize celestial objects.

One of the most fascinating aspects of Ray’s research is the potential link between 3I/ATLAS and the Osiris Rex mission, which successfully collected samples from the asteroid Bennu.
The findings from Bennu revealed the presence of organic compounds—building blocks of life such as RNA, DNA precursors, and amino acids.
This discovery has significant implications for astrobiology and our understanding of how life might arise on other planets.
If 3I/ATLAS is indeed an interstellar object, it could carry organic materials formed in entirely different stellar environments.
The prospect of encountering ancient relics of life from another star system is both thrilling and daunting.
Ray’s research suggests that if 3I/ATLAS is not just a comet but something more, the implications for our understanding of life’s origins could be profound.
Ray’s findings regarding 3I/ATLAS are particularly compelling when considering the data collected from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile.
The VLT’s spectroscopic analysis failed to detect any of the typical cometary signatures, such as hydroxyl (OH) and cyanogen (CN), which are fundamental markers for classifying an object as a comet.
The absence of these gases raises significant questions about the nature of 3I/ATLAS.
Moreover, Ray observed that after 3I/ATLAS reached perihelion (the point in its orbit closest to the sun), it exhibited sudden activity, producing jets and increasing in brightness.
This behavior contradicts the earlier analysis, suggesting that the object may have undergone a transformation that challenges our current understanding of solar system dynamics.
Adding to the intrigue, the Japanese JAXA Charism satellite detected X-ray emissions from 3I/ATLAS, further complicating the narrative.
X-ray emissions are typically associated with interactions between solar wind and cometary gases.
However, if 3I/ATLAS lacks those gases, the source of the X-rays remains a mystery.
This contradiction highlights the need for further investigation and raises questions about the object’s origin and composition.
Ray’s observations serve as a reminder that the universe is full of surprises, and our understanding of it is constantly evolving.
The data he has collected challenges established models and calls for a reevaluation of how we classify and interpret celestial objects.
Ray’s work on 3I/ATLAS exemplifies the value of independent research in the field of astrophysics.
As he navigates the complexities of this enigmatic object, he reminds us that science thrives on curiosity and skepticism.
The anomalies he has documented challenge the status quo and encourage us to look beyond conventional explanations.
In a world where institutional biases can shape scientific narratives, Ray’s observations are crucial.
They push us to ask difficult questions and explore possibilities that may seem uncomfortable.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, it’s essential to support independent researchers like Ray, who are willing to challenge established norms and seek the truth, no matter how elusive it may be.
News
The Boy Who Stopped Keanu Reeves: A Moment of Divine Intervention or Just a Child’s Fantasy?
The Boy Who Stopped Keanu Reeves: A Moment of Divine Intervention or Just a Child’s Fantasy? Keanu Reeves was ready…
The Moment That Defined a Legend: How Michael Jackson Saved His Brother Live on TV
The Moment That Defined a Legend: How Michael Jackson Saved His Brother Live on TV Jackie Jackson stood nervously on…
The Night Elvis Stood Up: How One Concert Changed History Forever
The Night Elvis Stood Up: How One Concert Changed History Forever Montgomery, Alabama, April 1969. The air inside the Montgomery…
The Miracle That Changed Everything: Pope Francis and the Girl Who Defied Death
The Miracle That Changed Everything: Pope Francis and the Girl Who Defied Death Maria had always been a bright and…
The Day a Joke Changed Music Forever: How Quincy Jones and Michael Jackson Created a Legend
The Day a Joke Changed Music Forever: How Quincy Jones and Michael Jackson Created a Legend The air was thick…
The Plantation Master Who Left Everything to His Slave and His Wife with Nothing: A Shocking Legacy
The Plantation Master Who Left Everything to His Slave and His Wife with Nothing: A Shocking Legacy The attorney’s hand…
End of content
No more pages to load