Elon Musk’s Bold Claim: Why NASA Has Never Returned to the Moon
The lunar landings of the late 1960s and early 1970s marked a monumental achievement in human history.
Apollo 11 gave the world a historic front-row seat to mankind’s first steps on the moon, as Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin etched their names into history.
However, despite this groundbreaking accomplishment, NASA’s plans to return to the lunar surface have remained stalled for decades.
From budget cuts to shifting priorities, the journey back to the moon has never fully materialized.

Now, Elon Musk has stated, “I will show you why NASA has never returned to the moon.”
So, let’s delve into the reasons behind NASA’s absence from the lunar surface since the last Apollo mission.
The Apollo program is often regarded as one of the most significant achievements in human history, not only for its technological feats but also for the incredible steps taken in human exploration.
While Apollo 11 often takes center stage due to its historic landing, the story of the Apollo program is much broader.
It was a decades-long effort that began in the early 1960s, involving numerous missions, groundbreaking technology, and a determined focus on advancing humanity’s capabilities in space.

The foundation of the Apollo program was laid in the early years of space exploration under NASA, which was formed in response to the Soviet Union’s early successes in space.
Before any astronaut could land on the moon, the program faced a major setback.
Apollo 1 was slated to be the first crewed mission of the Apollo program, intended to test the spacecraft systems in low Earth orbit.
However, on January 27, 1967, a tragic fire broke out during a pre-launch test, resulting in the loss of all three astronauts aboard—Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger B. Chaffee.
This devastating event led to a complete redesign of the Apollo Command Module and more thorough testing of both the spacecraft and its equipment.
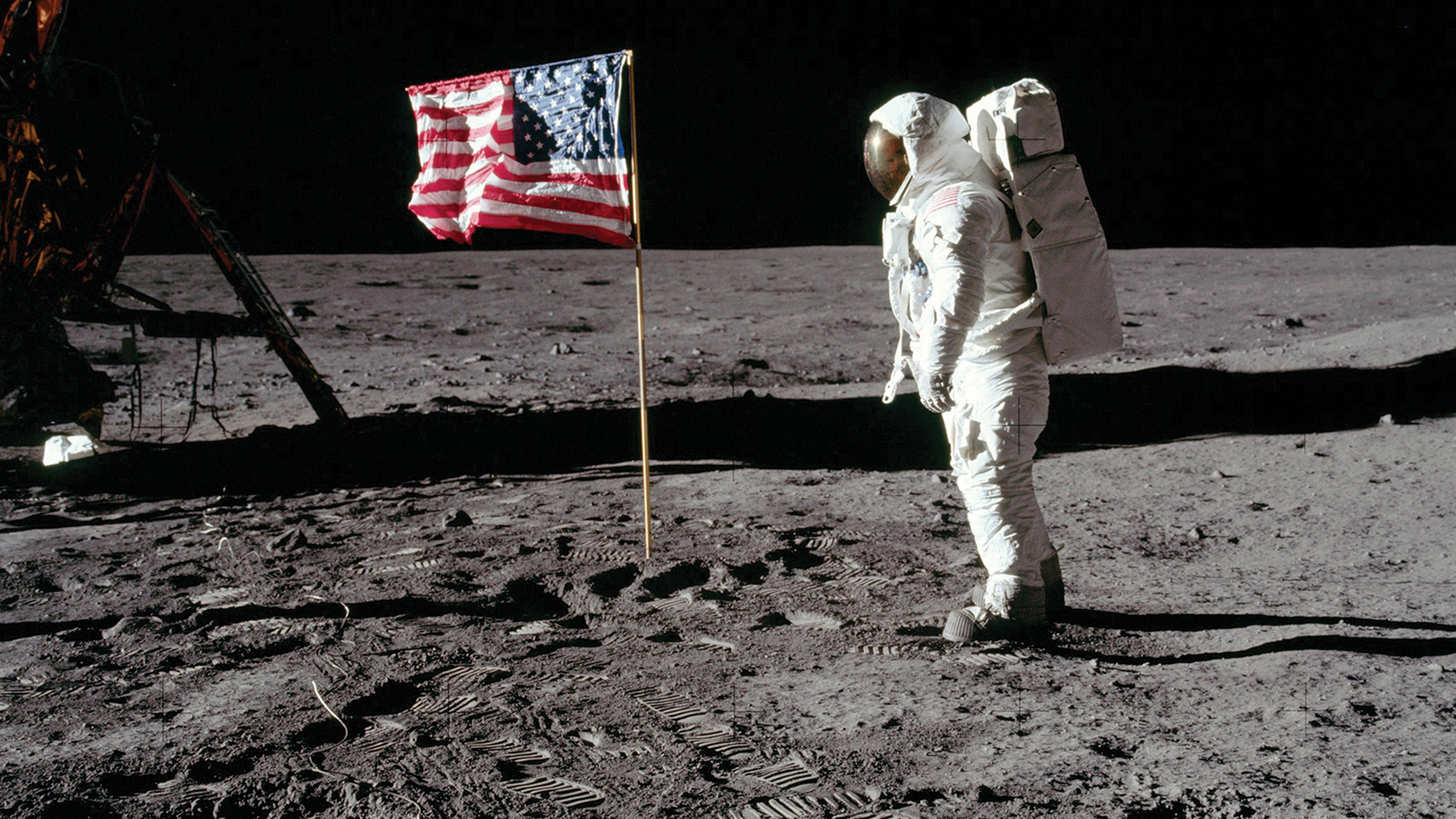
After the Apollo 1 disaster, NASA went to great lengths to address the issues that had contributed to the tragedy.
The crew’s sacrifice set the tone for the perseverance that would follow in later Apollo missions.
It wasn’t until October 1968—nearly two years after the Apollo 1 tragedy—that the program saw its first success.
Apollo 7 became the first crewed flight in the Apollo program, crucial for testing and developing the spacecraft systems that would eventually take astronauts to the moon.
The mission was a success, confirming that the spacecraft’s life support systems, guidance, and navigation worked as expected.
Apollo 8 made history by becoming the first mission to send astronauts around the moon.
This mission, which was not originally part of the Apollo program’s plan, was launched on December 21, 1968.
Upon reaching lunar orbit, the crew made a series of burns to adjust their trajectory and successfully entered a stable orbit around the moon.
This mission is especially significant as it marked the first time humans saw the far side of the moon and witnessed Earth rising above the lunar horizon.
After ten orbits of the moon, Apollo 8 returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968.
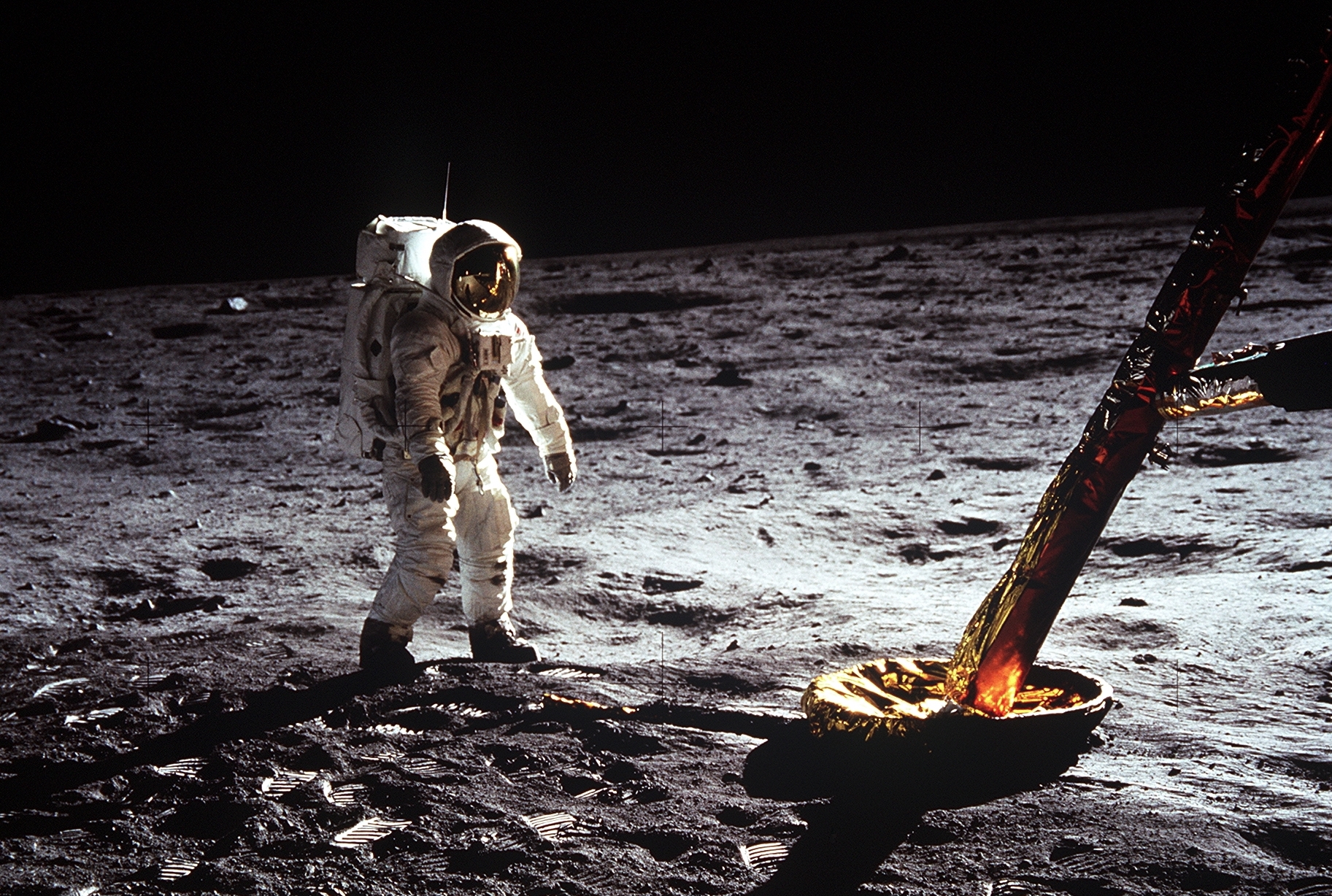

Apollo 9 was the first mission to test the lunar module, which would be used to land astronauts on the moon.
Apollo 10 served as a dress rehearsal for Apollo 11, testing the entire lunar landing sequence except for the actual landing itself.
The success of Apollo 10 paved the way for the historic landing of Apollo 11, which finally achieved the goal of putting humans on the lunar surface.
After the success of Apollo 11, several more crewed missions were sent to the moon, focused on lunar exploration and contributing to a deeper understanding of the moon’s geology and environment.
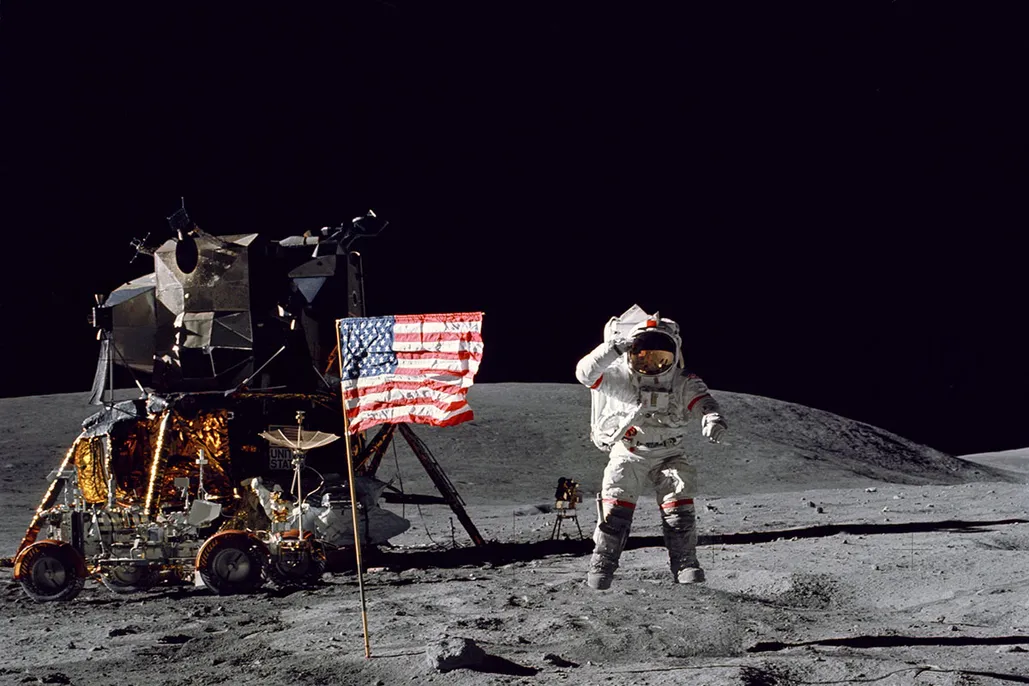
Apollo 17, launched in December 1972, was the last mission of the Apollo program.
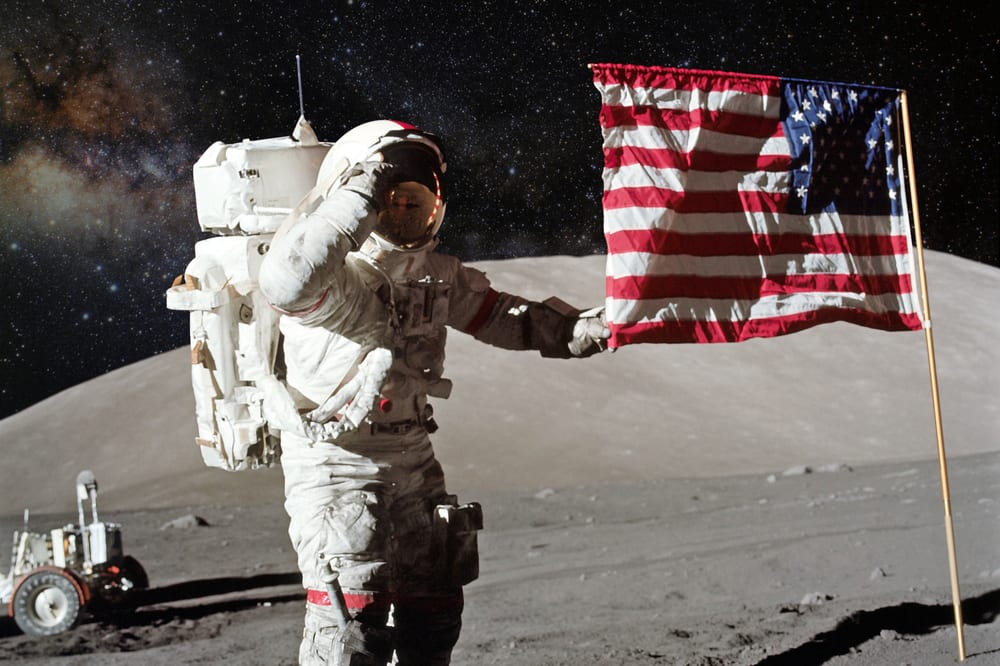

The crew spent three days on the lunar surface, exploring the Taurus-Littrow Valley, collecting samples, and conducting scientific experiments.
Apollo 17 remains the final time humans have traveled beyond Earth’s orbit, marking the end of an era in human exploration of the moon.
The Cold War moon race was marked by intense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasting from the end of World War II until the early 1990s.
Among the most fascinating arenas of this competition was the Space Race, which pitted the US and the USSR against each other in a technological and scientific contest.
The origins of the Space Race are tied to the broader context of the Cold War, where each side sought to prove its superiority militarily, economically, and ideologically.

The competition to achieve dominance in space was not just about technological innovation; it was a way for both nations to assert their political and ideological systems as superior.
The US championed capitalism and democracy, while the USSR promoted communism and a state-controlled economy.
The race to space became an extension of this ideological battle, with both nations eager to demonstrate that their way of life could produce greater achievements.
The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957, marked the beginning of the Space Race.
Sputnik was the world’s first artificial satellite, and its successful launch shocked the United States, demonstrating the USSR’s ability to send a man-made object into orbit.

This raised serious concerns about the technological and military capabilities of the Soviet Union.
If the Soviets could send a satellite into space, could they also develop the capability to launch nuclear missiles from space?
The launch of Sputnik spurred the US government into action, leading to the creation of NASA in 1958 as a direct response to the Soviet success.
The US was not only concerned with closing the technological gap but also with the implications of Soviet achievements in space, particularly regarding national security.
As both nations poured resources into their space programs, the Space Race became one of the defining features of the Cold War.
However, once the US landed on the moon with Apollo 11, the political will to continue funding lunar missions began to diminish.
Despite the groundbreaking success of the Apollo program, NASA did not send astronauts back to the moon after Apollo 17.
One key reason cited for halting lunar missions was the immense cost; at its peak, the Apollo program consumed roughly $25 billion—equivalent to over $50 billion today.
Public enthusiasm for space exploration also began to wane.
By the time Apollo 17 landed on the moon in 1972, the novelty of lunar exploration had worn off, and there were pressing issues facing the US, such as the Vietnam War and growing economic concerns.

As a result, public support for space exploration, especially lunar missions, began to decline.
The political landscape in the US shifted significantly after Apollo 17, and the Apollo program was, in many ways, a product of Cold War competition with the Soviet Union.
Once the objective of landing on the moon was achieved, the impetus to continue funding the Apollo missions diminished.
However, Elon Musk has challenged this narrative, asserting, “I will show you why NASA has never returned to the moon.”
He claims there is evidence suggesting NASA might have discovered something on the moon that they were not ready to confront.
Musk theorizes that it wasn’t just about shifting public opinion or reallocating resources; he hints at classified data from the Apollo missions that was never made public.
This raises questions about what NASA might have found on the moon’s far side—could it be alien structures, untapped resources, or something more ominous?
Elon Musk, with his bold ventures into space, promises to uncover the real reasons behind NASA’s absence, insisting that if there is a truth to be told, we owe it to humanity to find out.
This isn’t just speculation; Musk has reportedly directed SpaceX to prepare missions specifically aimed at the moon—not just to land humans there again but to investigate these unanswered questions.
Musk believes we can’t fully explore Mars until we understand what NASA left behind or why they never went back.
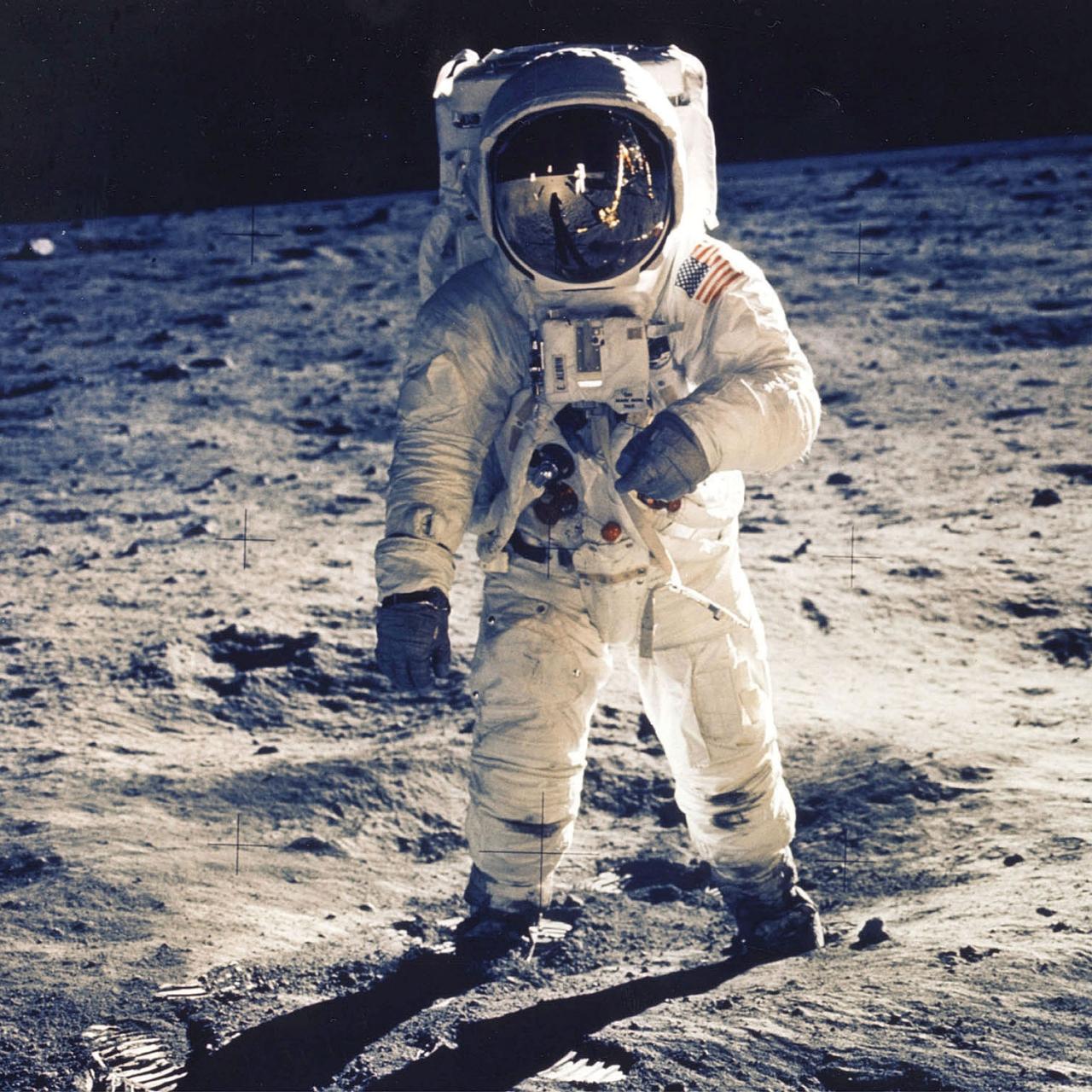

With SpaceX’s advanced Starship program, Musk believes we are closer than ever to uncovering the moon’s secrets.
Whether it’s a game-changing discovery or just a forgotten piece of history, Musk’s quest has reignited the debate about why NASA hasn’t returned to the moon and what they could be hiding.
Moreover, recent discoveries have shown that the moon is more dynamic than previously thought.
Scientists have found evidence of water and ice at the lunar poles, hidden within permanently shadowed craters.
This discovery could have vast implications; water is essential for human life and could be used for drinking, producing oxygen, or even creating hydrogen for rocket fuel.
These resources could enable a sustained human presence on the moon, potentially turning the lunar surface into a platform for further exploration of the solar system.

Evidence also suggests that the moon is not as dead as once thought; seismic activity has been detected, hinting at internal dynamics beneath the surface.
It’s possible that there are still untold geological processes happening on the moon, harboring crucial scientific secrets.
Another interesting find has been the discovery of rare geological formations on the moon’s surface, indicating signs of ancient volcanic activity and materials not found elsewhere in the solar system.
These findings could unlock new knowledge about the formation of planetary bodies and potentially human settlements on the moon.
Could it be true that NASA never returned to the moon because of what they found or what they couldn’t explain?
Elon Musk’s revelations leave us with more questions than answers, but one thing is clear: he is determined to uncover the truth.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
News
Pierce Brosnan Is Saying Goodbye After His Wife’s Tragic Diagnosis – HTT
Pierce Brosnan’s Heartbreaking Journey: Facing Loss, Love, and Legacy Pierce Brosnan, the iconic actor best known for his role as…
Russell Westbrook’s POWERFUL Message Left Nikola Jokic SPEECHLESS – HTT
How Russell Westbrook’s Unexpected Praise Left Nikola Jokic Speechless and Redefined Their Partnership In an NBA world filled with intense…
Trump LOSES IT After Supreme Court’s GAME CHANGING Ruling! – HTT
Trump’s Furious Meltdown After Supreme Court Slams His “Unlimited Immunity” Fantasy In a stunning legal showdown, the United States Supreme…
Just Happened! Elon Musk Revealed ALL-NEW 2 Shock Batteries Tech, Destroy Entire Industry! (MIX) – HTT
Revolutionizing EVs: Elon Musk and CATL’s Breakthrough Battery Technologies Set to Disrupt the Industry The electric vehicle (EV) industry stands…
Heartbreaking News For Fox News’ Kat Timpf Is Just So Sad – HTT
The Unseen Battle of Fox News’ Kat Timpf: A Story of Strength Amid Heartbreak Kat Timpf, the sharp-witted Fox News…
It Happened! Elon Musk Confirms All-New Specs, Final Price And Production Plan Tesla Model 2! – HTT
Tesla Model 2 Unveiled: Elon Musk Confirms Specs, Pricing, and Production Plans for 2025 Tesla has officially lifted the curtain…
End of content
No more pages to load



















